In classical physics, causality (the fact that a cause always precedes its effect) was considered a rule imposed on space and time. Albert Einstein's (1879-1955) vision changed everything.
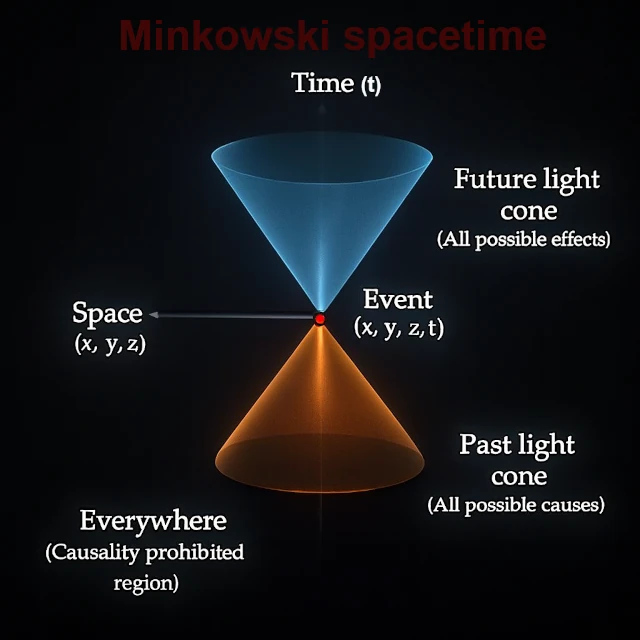
In special and general relativity, spacetime is not a mere backdrop: it is organized in such a way as to ensure that cause-and-effect relationships always respect a logical order. This organization is embodied by a fundamental geometric object: the light cone. It delimits, around each event, the areas where causes can act and where effects can occur, prohibiting any interaction that would violate the speed of light, and thus, the causal chronology.
Each point in spacetime, each moment in the Universe, is at the apex of a double light cone, thus structuring the limits of its past and future influence.
Imagine an event (such as turning on a flashlight in space). The light cone represents all possible trajectories of light rays emitted by this source. In other words, this geometry determines what is possible and impossible to explain this event. If an event is outside your light cones, it cannot influence you and you cannot influence it. It is causally disconnected from you.
N.B.:
In relativity, the intervals between two events are classified into three fundamental categories: timelike (inside the light cones, where causality is possible), lightlike (on the surface of the cones, accessible only at the speed of light), and spacelike ("elsewhere," outside the cones, where no causal interaction can exist).
The "elsewhere" (spacelike region) is the domain of the causal impossible. Each event has an "elsewhere." This is the zone of mutual exclusion between the double cones of two events that are too far apart in space relative to the time separating them.
Thus, two events separated by a spacelike region cannot be linked by a cause or effect. In the "elsewhere" region, sending a signal or any message would require exceeding the speed of light, which is impossible.
An astronaut on Mars (about 20 light-minutes away) sends a radio message to Earth. During the 20 minutes the message travels, the astronaut and Earth controllers live in causally separated "presents." What Earth does during these 20 minutes cannot affect the astronaut's decision to send the message, and vice versa. They are temporarily in their respective "elsewhere" and neither can be the cause of the other.
Spacetime is a vast fabric woven by intertwined light cones, where each event, each moment, is the center of a double cone that delimits its history and possible future. An organized hubbub, where the very geometry of the Universe ensures that cause and effect never get lost in chaos.
In this sense, spacetime reveals itself through the network of events: without these anchor points where past and future intertwine, the Universe would lose its causal framework and its physical meaning.
For events that are causally linked (one is in the other's light cone), all observers agree on the order of events: the cause always precedes the effect.
For events that are not causally linked, the order can reverse depending on the observer.
Earth and the Moon send a laser beam to each other at exactly the same time t=0. (Earth-Moon distance: ~384,400 km, Speed of light: ~300,000 km/s, Light travel time: ~1.28 seconds).
The principle that the cause always precedes the effect is not just a convention, but a fundamental constraint of spacetime. Light cones, relativity, and the very structure of the Universe make it an inviolable law: without this order, causality would collapse, and with it, our ability to understand reality. In this sense, the arrow of time and the logic of events are not illusions, but the invisible pillars on which the coherence of the world rests.