When looking into the past, the universe is smaller, denser, and hotter. In other words, all objects in the Universe move closer to each other when watching the film in reverse, going back in time.
In 1923 Edwin Hubble (1889-1953) used the 250 cm Hooker telescope, the most powerful telescope of the time. Observations made with this telescope allowed Hubble to establish that the nebulae previously observed with less powerful telescopes were not part of our Galaxy. Indeed, he determined the distance of the Andromeda galaxy (M31), which he evaluated at 800,000 light-years, placing it outside our galaxy. Thus, Hubble ended the long debate on the nature of the diffuse objects that would henceforth be called galaxies.
A little later, in 1929, Hubble analyzed the radial velocities of galaxies, previously measured by Vesto Slipher (1875-1969), based on the redshifts of spectral lines. He initially limited himself to galaxies located less than 6 million light-years away and noticed that the velocity-distance relationship was approximately linear. Along with Milton Humason (1891-1972), he extended his study to galaxies up to 100 million light-years away, and the relationship remained linear.
Hubble then stated his famous law, "Galaxies move away from each other at a velocity proportional to their distance". In other words, the farther a galaxy is from us, the faster it seems to move away. He thus created the concept of the expansion of the Universe. Note that galaxies move away, but it is not a real movement of the galaxies; it is the entire Universe that is expanding and giving this apparent velocity to the galaxies. It is the space between the galaxies that is increasing; in reality, it is spacetime that is expanding.
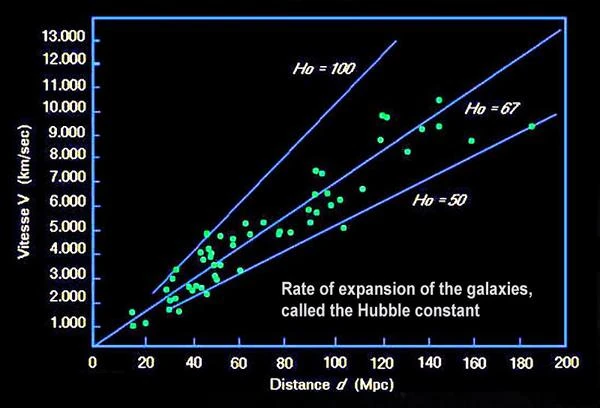
The rate of expansion of galaxies relative to each other corresponds to the Hubble constant (Hο) calculated by Edwin Hubble and Georges Lemaitre in the 1930s. The inverse of the Hubble constant is called the "Hubble time," which corresponds to the duration since the Big Bang, i.e., the age of the universe. The cosmic microwave background, discovered in 1965, is a true "Rosetta Stone" for cosmologists, as it allows deciphering the thermal history of the Universe since the Big Bang.
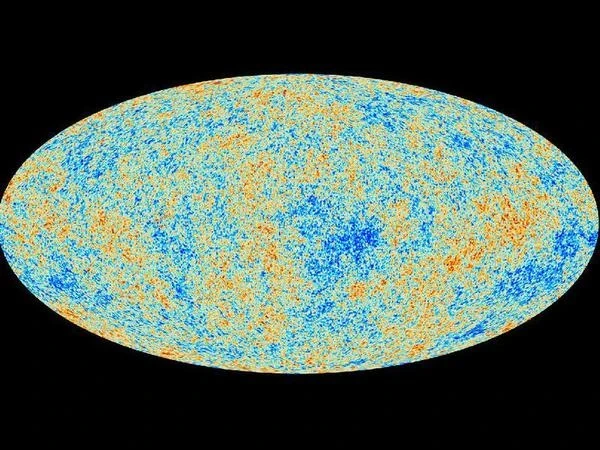
The map of the Cosmic Microwave Background represents the electromagnetic radiation from the first moments of the observable Universe. These photons, detectable today in the radio wave range, have retained the traces of the emerging large structures that will be carried by inflation.
The value of the Hubble constant (Hο) is not known precisely. All measurements made since the 2000s give a value between 63 km/s/Mpc and 73 km/s/Mpc. In March 2013, the Planck satellite, whose mission is to reconstruct the thermal history of the Universe, calculated a value of 67 km/s/Mpc. In other words, a bubble of 1 Mpc, i.e., 3.26 light-years, expands by 67 km every second, a bubble of 10 Mpc expands by 670 km every second, a bubble of 100 Mpc expands by 6700 km every second…
The expansion of the universe only applies to very large spaces, i.e., between entities such as galaxy clusters or superclusters.
In the solar system, objects are "connected" by the gravitational force of the Sun, and the whole can be considered a compact system.
Objects with mass and whose velocity relative to each other is less than their escape velocity are part of a gravitational system. As long as the system is gravitationally bound, the space between the objects cannot expand under the effect of an antigravitational force. The entire system is decoupled from the expansion of the observable Universe. The same applies to the Sun within the Galaxy.
| Units of distances | pc | al | au | km |
| pc | 1 | 3,26 | 206265 | 3,09x1013 |
| al | 0,307 | 1 | 63242 | 9,46x1012 |
| au | 4,85x10-6 | 1,58x10-5 | 1 | 1,50x108 |
| km | 3,24x10-14 | 1,06x10-13 | 6,68x10-9 | 1 |