After the COBE satellite launched in November 1989, WMAP in June 2001, the Planck probe launched in May 2009 continued to explain the history of the Universe with increasingly finer resolution.
The Universe contains everything that exists, including space-time, so it has no "edge." Indeed, the existence of an edge would imply that beyond this edge, one would no longer be in the Universe. Will we cross this observable limit?
The observable limit is a "radio whisper" captured by various satellites in the electromagnetic spectrum at 2.7K (-270°C). It shows us the residual fluctuations of our universe and, in the background, the clumps of matter that gave rise to galaxies, stars, and everything we currently see. Thanks to the fossil electromagnetic radiation or Cosmic Microwave Background, detected fortuitously by Arno Allan Penzias and Robert Woodrow Wilson in 1965, we can see our past.
Ralph Alpher (1921-2007) and Robert Herman (1914-1997), supported by George Gamow (1904-1968), predicted in 1948 the existence of radiation from the Big Bang. The fossil radiation is a natural microwave radiation at low temperature reaching the Earth's surface from all directions of the cosmos. It is called this because it forms a background to all the point radio sources that have been detected by radio telescopes.
This residual radiation from the cosmic background was not emitted at the birth of the Universe but at the moment when the Universe transitioned from an opaque state to a transparent, i.e., luminous, state. Before this, the Universe was invisible, not composed of matter (neutrons and protons), but of a soup of quarks and gluons.
380,000 years after the Big Bang, light began to travel freely for the first time. The light from the gigantic fireball that followed the Big Bang slowly cooled to become, 13 billion years later, a microwave background. The Observable Universe contains approximately 7×1022 stars, spread across about 1011 galaxies, which are themselves organized into clusters and superclusters of galaxies. The number of galaxies could be even greater. This is why cosmology specialists often use the term observable universe.
N.B.:
The Big Bang model favors the existence of a very brief phase of cosmic inflation during which the universe would have grown extremely rapidly. It is from this point that most of the material particles of the universe were created at high temperature, triggering the emission of a large amount of light, called the cosmic microwave background. This radiation is now observed with great precision by space probes.
Light does not travel at infinite speed, so the observations we make come from the past.
By looking further and further away, we see objects as they were in the past, closer and closer to the time of the Big Bang.
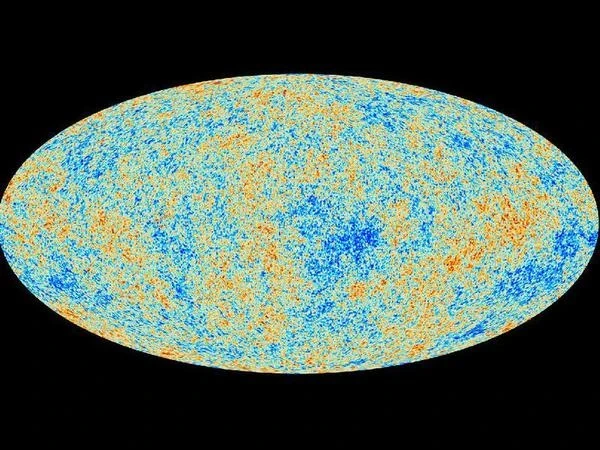
Here is the best-ever representation of the observable Universe (March 2013). This map shows the oldest cosmic beacon radiating in our universe. Thanks to the Planck mission, this trace of the first cosmic objects has been detected with such precision.
The ancient light (cosmic microwave background) was imprinted on this map when the Universe was only 380,000 years old. The image displays tiny temperature fluctuations corresponding to regions of slightly different densities, each representing the seeds of all future structure in the Universe, i.e., today's stars and galaxies.
By analyzing the patterns of light on this map, scientists have refined what we know about the universe, its origins, future, and basic components. Scientists have cleaned this representation of all the light emitted by surrounding galaxies and our own Milky Way.
Planck allowed us to set a more precise age for our Universe (13.8 billion years), slightly older than that of WMAP (13.75 billion years). Its composition has also been refined: 4.8% ordinary matter (atoms), 25.8% dark matter, and 69.4% dark energy.
The vast amount of data collected by Planck will keep researchers busy for many years and will undoubtedly reveal more secrets about the creation of matter. On July 3, 2009, Planck reached the Lagrange point L2 and was placed in a trajectory called a Lissajous orbit. L2 is located 1.492 million km from Earth, opposite the Sun. The satellite should rotate slower than Earth because the solar gravitational force is weaker, but Earth's gravitational field tends to accelerate it. At point L2, the object orbits the Sun at the same angular velocity as Earth.
N.B.:
The first glimmers of the observable universe seen by the Planck mission (March 2013). This image represents traces of the first moments of creation about 380,000 years after the Big Bang. European, Canadian, and American astrophysicists from the mission worked together to analyze the enormous flow of data from the Planck space telescope. Planck observes and measures temperature variations in the microwave background with much higher sensitivity, better angular resolution, and over a broader range of frequencies than all previous observatories.