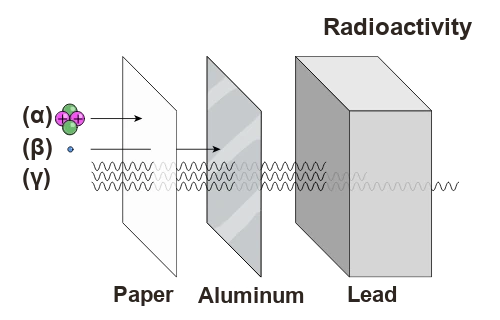
Radioactivity is a natural or artificial phenomenon where certain unstable atomic nuclei release energy in the form of particles or radiation. This energy emission can be classified into three main types: alpha, beta, and gamma. Each of them has unique characteristics.
Alpha radioactivity is a type of radiation composed of alpha particles, which are helium nuclei (two protons and two neutrons). These particles are relatively heavy and positively charged.
Alpha particles are emitted by heavy nuclei such as Uranium, Thorium, Radon, Polonium, Plutonium, Radium, etc.
Alpha particles have a low penetration capability and can be stopped by a simple sheet of paper or even by human skin. Due to their high ionizing energy, once inside the body, these particles interact directly with the cells of internal tissues and can cause significant damage to cells (damage DNA or destroy tissues).
To protect against alpha radioactivity, it is recommended to use physical barriers such as gloves, protective clothing, and masks to avoid inhaling or ingesting alpha particles.
Beta radioactivity consists of beta particles, which are electrons or positrons emitted by unstable atomic nuclei. These particles are lighter and more penetrating than alpha particles.
Beta particles are emitted by Potassium-40 (K-40) present in rocks, soil, and living organisms, Carbon-14 (C-14) and Tritium (H-3) formed in the Earth's atmosphere by the interaction of cosmic rays with nitrogen, and Rubidium-87 (Rb-87) present in many minerals.
Beta particles can be stopped by a sheet of aluminum or thick plastic. They can penetrate human skin to a certain depth, but they are less dangerous than alpha particles if ingested or inhaled.
To protect against beta radioactivity, it is advisable to use protective barriers such as latex gloves, protective clothing, and screens made of plastic or aluminum.
Gamma radioactivity is a type of high-energy electromagnetic radiation, similar to X-rays but with even higher energy. Gamma rays are very penetrating and can pass through several centimeters of lead or concrete.
Gamma rays are emitted at each stage of the decay chain of Uranium-238 (U-238), Thorium-232 (Th-232), Potassium-40 (K-40), Radon-222 (Rn-222), and also from space (cosmic radiation).
Gamma rays are extremely dangerous because they can penetrate deeply into the human body and damage cells. They require very thick protective barriers, such as concrete walls or lead screens, to be stopped.
To protect against gamma radioactivity, it is essential to use dense and thick materials (lead, concrete, steel, tungsten, ceramics, etc.). Special protective clothing and radiation shelters are also necessary in environments with high gamma radioactivity.
| Characteristic | Alpha Radiation (α) | Beta Radiation (β) | Gamma Radiation (γ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nature | Helium nucleus (2 protons + 2 neutrons) | Electron (β⁻) or positron (β⁺) | High-energy photon (electromagnetic wave) |
| Electric charge | +2 | -1 (β⁻) or +1 (β⁺) | 0 |
| Relative mass | High (4 u) | Low (≈ 1/1836 u) | None |
| Penetration power | Low (stopped by a sheet of paper) | Medium (stopped by a few mm of aluminum) | High (requires several cm of lead) |
| Ionizing power | Very strong | Moderate | Weak |
| Speed | Low (≈ 5% of c) | High (≈ 90% of c) | c (speed of light) |
| Origin | Emission by heavy unstable nuclei | Beta decay of radioactive nuclei | Nuclear de-excitation after alpha or beta emission |
| Biological hazard | Low at distance, high if ingested or inhaled | Moderate | High even at a distance |
Reference:
• Krane K. S., Introductory Nuclear Physics, Wiley, 1987.
• Halliday D., Resnick R., Walker J., Fundamentals of Physics, 10th Edition, Wiley, 2013.