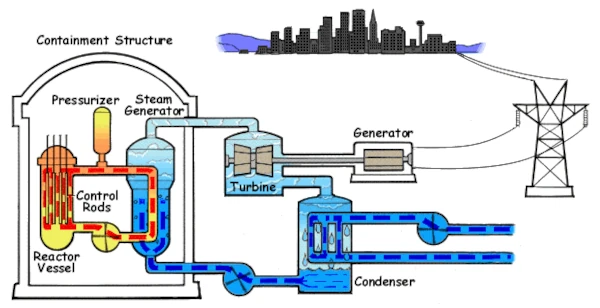
The basic principle of a nuclear power plant is based on the fission of heavy atoms, particularly uranium-235. When a uranium-235 nucleus absorbs a neutron, it becomes unstable and splits into two lighter nuclei, releasing a large amount of energy (about 200 MeV) as well as several additional neutrons. These neutrons can, in turn, cause further fissions: this is the chain reaction.
A nuclear power plant mainly consists of:
Control of the chain reaction is ensured by control rods, made of materials that absorb neutrons (boron, cadmium). By inserting or removing these rods from the reactor core, the number of fissions is modulated. In an emergency, an automatic shutdown (scram) allows these rods to be inserted instantly to stop the reaction. The containment structure, often made of prestressed concrete, prevents radioactive releases in case of an accident.
| Reactor Type | Moderator | Cooling | Fuel | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PWR (Pressurized Water Reactor) | Light Water | Pressurized Water | Enriched UO₂ (~3-5% U-235) | PWR – France (EDF) |
| BWR (Boiling Water Reactor) | Light Water | Boiling Water | Enriched UO₂ | BWR – Japan, USA |
| RBMK | Graphite | Light Water | Natural Uranium | Chernobyl – USSR |
| PHWR (CANDU) | Heavy Water | Heavy Water | Natural Uranium | Canada |
Sources: International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), World Nuclear Association
Nuclear energy has many advantages: continuous production, low CO₂ emissions, high energy density. However, it raises issues of safety, radioactive waste management, and proliferation. The lifespan of waste (up to several hundred thousand years for some isotopes like plutonium-239) implies intergenerational responsibility.
Fourth-generation reactors are under development (fast breeders, molten salts, high temperature) to improve safety, reduce waste, and optimize resources. At the same time, nuclear fusion – particularly via the ITER project – promises abundant energy, without long-lived waste, but remains at the experimental stage.
| Country | Nuclear Production (TWh) | Share of Nuclear in the Country | Share of Global Nuclear Production |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | ≈ 775 TWh | 18.5% | ≈ 30.5% |
| China | ≈ 433 TWh | 4.9% | ≈ 17.0% |
| France | ≈ 324 TWh | 64.8% | ≈ 12.6% |
| Russia | ≈ 217 TWh | 18.4% | ≈ 8.5% |
| South Korea | ≈ 180 TWh | 30.7% | ≈ 7.1% |
| Ukraine | ≈ 86 TWh | ≈ 55% | ≈ 3.4% |
| Canada | ≈ 85 TWh | ≈ 13.7% | ≈ 3.3% |
| Japan | ≈ 77 TWh | ≈ 5.5% | ≈ 2.2% |
| Spain | ≈ 54 TWh | ≈ 20.3% | ≈ 2.1% |
| India | ≈ 48 TWh | ≈ 3.1% | ≈ 1.9% |
| Sweden | ≈ 47 TWh | ≈ 28.6% | ≈ 1.8% |
| United Kingdom | ≈ 37 TWh | ≈ 12.5% | ≈ 1.5% |
| United Arab Emirates | ≈ 33 TWh | ≈ 19.7% | ≈ 1.3% |
| Finland | ≈ 33 TWh | ≈ 42% | ≈ 1.3% |
| Belgium | ≈ 31 TWh | ≈ 41.2% | ≈ 1.2% |
| Czech Republic | ≈ 30 TWh | ≈ 40% | ≈ 1.2% |
| Pakistan | ≈ 24 TWh | ≈ 17.4% | ≈ 0.9% |
| Switzerland | ≈ 23 TWh | ≈ 32.4% | ≈ 0.9% |
| Slovakia | ≈ 18 TWh | ≈ 61.3% | ≈ 0.7% |
| Taiwan | ≈ 17.8 TWh | ≈ 6.3% | ≈ 0.7% |
| Brazil | ≈ 14.5 TWh | ≈ 2.2% | ≈ 0.6% |
| Hungary | ≈ 15 TWh | ≈ 48.8% | ≈ 0.6% |
Sources: IAEA PRIS "Operating Experience 2023" and World Nuclear Association "World Nuclear Industry Performance Report 2024"