Hominins include all species related to modern humans (Homo sapiens) after their divergence from the chimpanzee lineage. Paleogenetic analyses and fossils suggest that this split occurred between 7 and 6 million years ago, during a period of major climatic transformations in Africa.
The first recognized representative is Sahelanthropus tchadensis (≈ 7 Ma), discovered in Chad. Its skull, featuring an advanced foramen magnum, indicates a partially bipedal posture. It is followed by Orrorin tugenensis (≈ 6 Ma, Kenya) and Ardipithecus kadabba (5.8–5.2 Ma), which already show locomotor adaptations indicating a transition from an arboreal lifestyle to bipedalism.
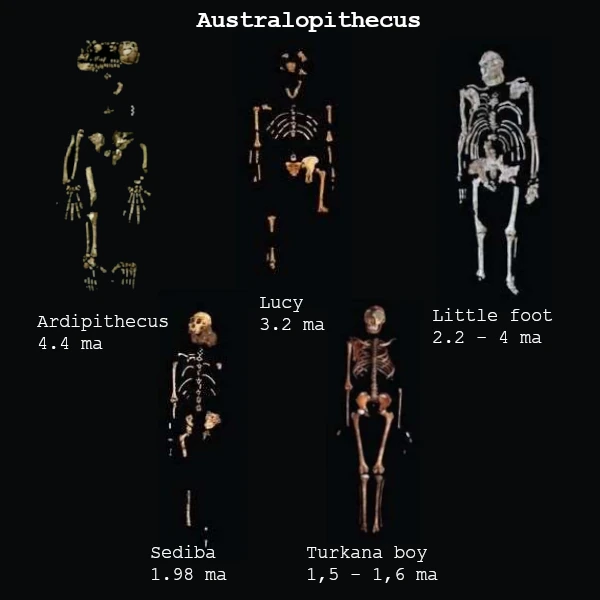
Between 4.5 and 2 million years ago, australopithecines emerged as the dominant hominins. Australopithecus afarensis (3.9–3.0 Ma), known from the famous "Lucy" fossil, embodies more pronounced bipedalism, although its cranial capacity (~400 cm³) remains close to that of great apes. These species were contemporary with ecological diversification, occupying varied niches from wooded environments to more open savannas.
Around 2.5 million years ago, the appearance of the genus Homo marked a major evolutionary turning point. Homo habilis and Homo rudolfensis are associated with the first lithic tools (Oldowan industry), indicating new cognitive abilities. Soon after, Homo erectus (1.9 Ma) became the first great colonizer of the world, leaving Africa to populate Asia and Europe, mastering fire, and developing organized societies.
Over the last million years, the human lineage became more complex with Homo heidelbergensis, Homo neanderthalensis, the mysterious Denisovans, and island species such as Homo floresiensis and Homo luzonensis. Finally, Homo sapiens, which appeared in Africa about 300,000 years ago, is distinguished by the emergence of symbolic language, art, and cumulative culture, leading to today's planetary diversity and dominance.
Thus, the evolution of hominins, spanning over 7 million years, illustrates a complex process of diversification and extinction, where several species coexisted before our species became the sole survivor of the genus Homo. This bushy evolution demonstrates that humanity is not the result of linear progression, but of an intertwining of parallel lineages shaped by natural selection, climate, and culture.
| Species | Period (Ma) | Main Location | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sahelanthropus tchadensis | ~7.0 | Chad | Flat skull, position of the foramen magnum suggesting partial bipedalism |
| Orrorin tugenensis | 6.0 | Kenya | Femur adapted to bipedalism, primitive teeth |
| Ardipithecus kadabba | 5.8 – 5.2 | Ethiopia | Transition between arboreal primates and bipeds |
| Ardipithecus ramidus | 4.4 | Ethiopia | Mixed arboreal and bipedal, prehensile hands |
| Australopithecus anamensis | 4.2 – 3.9 | Kenya | Confirmed bipedalism, primitive dentition |
| Australopithecus afarensis | 3.9 – 3.0 | Ethiopia, Tanzania | Lucy; efficient bipedalism, cranial volume ~400 cm³ |
| Australopithecus prometheus (Little Foot) | 3.67 | South Africa (Sterkfontein) | Almost complete skeleton, bipedalism and arboreal life |
| Australopithecus bahrelghazali | 3.5 | Chad | Discovered far from the Rift Valley, diverse adaptations |
| Australopithecus africanus | 3.0 – 2.1 | South Africa | Skull of the Taung child, developed bipedalism |
| Australopithecus garhi | 2.5 | Ethiopia | Associated with the first lithic tools |
| Australopithecus sediba | 2.0 | South Africa | Intermediate traits between australopithecines and Homo |
| Paranthropus aethiopicus | 2.7 – 2.3 | Kenya | Black skull, marked sagittal crest |
| Paranthropus boisei | 2.3 – 1.2 | East Africa | Massive jaws, specialized vegetarian diet |
| Paranthropus robustus | 2.0 – 1.5 | South Africa | Very wide teeth, adaptation to grinding |
| Homo habilis | 2.4 – 1.6 | East Africa | First user of Oldowan tools |
| Homo rudolfensis | 2.4 – 1.8 | Kenya | Larger cranial volume than H. habilis |
| Homo erectus | 1.9 – 0.1 | Africa, Asia, Europe | First great migrant out of Africa, mastery of fire |
| Homo antecessor | 1.2 – 0.8 | Spain | Possible common ancestor of Neanderthals and Sapiens |
| Homo heidelbergensis | 0.7 – 0.2 | Europe, Africa | Organized hunter, probable ancestor of H. sapiens and H. neanderthalensis |
| Homo floresiensis | 0.1 – 0.06 | Indonesia (Flores) | "Hobbit", small size (~1 m), reduced brain |
| Homo naledi | ~0.3 | South Africa | Probable ritual funerary behavior |
| Homo luzonensis | 0.07 | Philippines | Island species, mix of archaic traits |
| Homo neanderthalensis | 0.4 – 0.04 | Europe, Asia | Complex culture, probable articulated language |
| Homo longi | 0.3 – 0.15 | China | "Dragon Man", close to Neanderthals and Denisovans |
| Homo sapiens | 0.3 – present | Africa then worldwide | Symbolic language, abstract thought, cumulative culture |
Sources: Smithsonian Human Origins Program, MNHN Paris, Leakey Foundation, Berger et al. (2015), Stringer (2022).