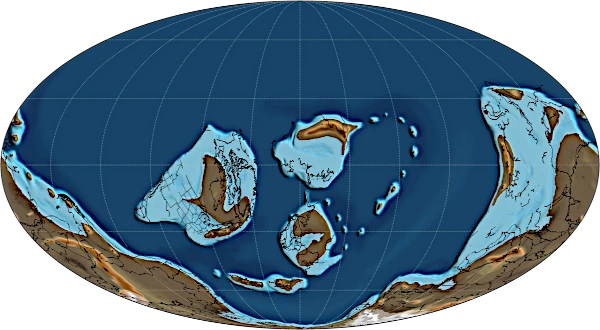
The Ordovician is the second geological period of the Paleozoic Era, spanning from ~485 to ~443 million years ago. This period follows the Cambrian and precedes the Silurian. It is a key time marked by a major diversification of marine life and significant tectonic and climatic changes.
| Geological Era | Approximate Period (millions of years) | Main Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Precambrian | ≈ 4600 to 541 Ma | Formation of Earth, appearance of the first unicellular life forms |
| Paleozoic | ≈ 541 to 252 Ma | Cambrian explosion, colonization of continents, development of marine and terrestrial life |
| Mesozoic | ≈ 252 to 66 Ma | Age of dinosaurs, evolution of the first mammals and birds |
| Cenozoic | ≈ 66 Ma to present | Development of modern mammals, human evolution |
During the Ordovician, Earth initially experienced a globally warm climate, with high atmospheric CO\(_2\) levels favoring a high, shallow sea that covered much of the continents. Towards the end of the period, a gradual cooling set in, leading to the first major known glaciation, particularly on the continent of Gondwana, then located at the South Pole.
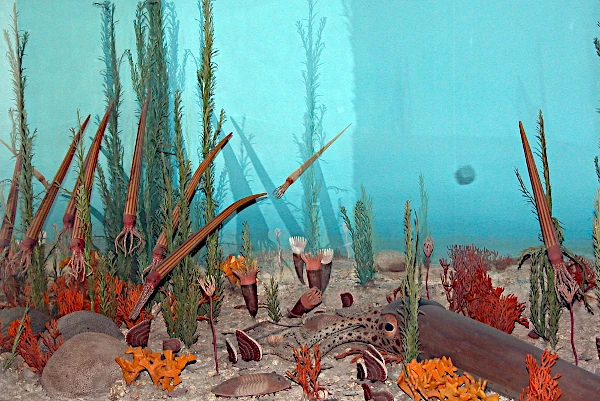

Marine life exploded in diversity during the Ordovician, a phenomenon often called the "Ordovician radiation". Trilobites, brachiopods, graptolites, and the first reef corals multiplied. The first primitive forms of fish also appeared. This biological dynamism was accompanied by a complexification of marine food chains.
The Ordovician ended with a major mass extinction, affecting nearly 85% of marine species, linked to intense climatic cooling and glaciation. This extinction profoundly altered the composition of marine ecosystems and paved the way for evolution in the Silurian.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Age | 485 to 443 million years ago |
| Duration | About 42 million years |
| Climate | Warm at the beginning, marked cooling at the end of the period |
| Dominant marine fauna | Trilobites, brachiopods, graptolites, first fish |
| Notable event | Ordovician-Silurian mass extinction (~85% of marine species) |