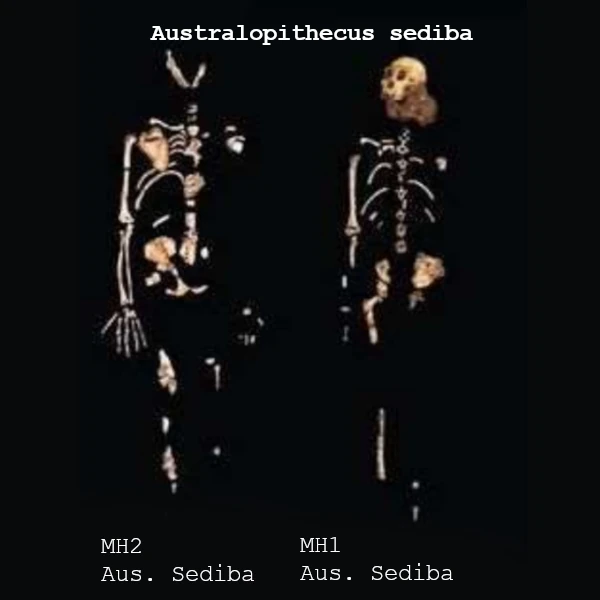
The Karabo skeleton, discovered in South Africa by Lee Berger in the 2000s, represents an Australopithecus sediba. Dated to about 2 million years ago, it combines primitive traits of australopithecines with features close to the genus Homo. This morphological mosaic makes it a key element in understanding the evolutionary transition to modern humans.
Karabo has a pelvis and legs adapted to bipedalism, but retains long arms and prehensile hands for climbing. The cranial capacity is estimated at 420–450 cm³, suggesting a brain slightly smaller than that of early Homo. Its study provides clues about the evolution of locomotion and feeding behavior.
To date, the skeleton of Karabo is one of the best-preserved Australopithecus sediba. More than 200 fossil fragments have been found in the Malapa Cave, South Africa, representing almost the entire adult skeleton. This exceptional abundance allows for precise study of the morphology, locomotion, and development of the species. The fossils include the skull, pelvis, upper and lower limbs, as well as teeth, offering a unique insight into daily life and physical abilities of Karabo.
N.B.:
The discovery of several hundred fragments is rare for Australopithecines and allows for almost complete reconstructions, unlike the more common fragmentary fossils.
| Species | Period (Ma) | Main Location | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Australopithecus afarensis | 3.9 – 3.0 | Ethiopia, Tanzania | Lucy; efficient bipedalism, cranial capacity ~400 cm³ |
| Australopithecus africanus | 3.0 – 2.1 | South Africa | Taung Child skull, developed bipedalism |
| Australopithecus sediba (Karabo) | 2.0 | South Africa | Mosaic of traits: advanced bipedalism and arboreal life, brain ~420–450 cm³ |
| Homo habilis | 2.4 – 1.6 | East Africa | First user of Oldowan stone tools |
| Homo erectus | 1.9 – 0.1 | Africa, Asia, Europe | First major migrant out of Africa, mastery of fire |
| Homo sapiens | 0.3 – present | Africa then worldwide | Symbolic language, abstract thought, cumulative culture |
Sources: Berger et al. (2010), Smithsonian Human Origins Program, MNHN Paris, Stringer (2022).