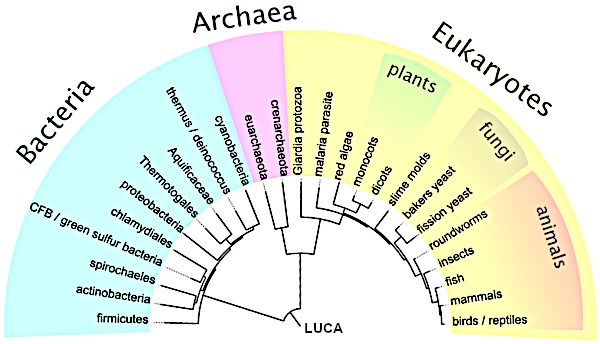
The last universal common ancestor, or LUCA, represents the hypothetical organism from which all current living beings on Earth descend. Research suggests that LUCA lived about 3.5 to 3.8 billion years ago, shortly after the formation of the oceans. Comparative genomic studies have identified about 355 genes that were probably present in LUCA.
From LUCA, life diversified into three major domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. Molecular analyses show that Archaea and Eukarya share a more recent common ancestor with each other than with Bacteria.
| Characteristics | Bacteria | Archaea | Eukarya |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell type Defines the basic structure of the cell | Prokaryote | Prokaryote | Eukaryote |
| Nucleus The nucleus contains DNA in eukaryotes | ❌ No | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Membrane-bound organelles Ex. mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum | ❌ No | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Cell membrane Type of lipids that make up the membrane | Ester lipids Less stable, typical of bacteria | Ether lipids Very stable, adapted to extreme environments | Ester lipids Like bacteria, but with cholesterol |
| Cell wall Rigid structure surrounding the cell | Peptidoglycan Polymer specific to bacteria | Pseudo-peptidoglycan Similar structure but chemically different | Cellulose, chitin, or absent Varies by type of eukaryote |
| Ribosomes Sites of protein synthesis | 70S Small, typical of prokaryotes | 70S Similar to bacteria but with subtle differences | 80S Larger, specific to eukaryotes |
| Intronic genes Presence of introns in genes | ❌ Rare Compact genome | ✅ Sometimes Similarities with eukaryotes | ✅ Frequent Introns present in most genes |
| Genetic organization Form of DNA in the cell | Circular DNA | Circular DNA | Linear DNA |
| Reproduction Mode of cell multiplication | Asexual By binary fission | Asexual Often by fission | Sexual or asexual Meiosis, mitosis, or simple division |
| Habitats Natural environment | Everywhere Soil, water, living organisms | Extreme environments Hot springs, saline, acidic | Varied environments Terrestrial, aquatic, aerial |
| Examples Representative organisms | Escherichia coli, Streptococcus | Halobacterium, Methanopyrus | Humans, plants, fungi |
The appearance of eukaryotic cells marks one of the major turning points in the history of life. Unlike prokaryotic cells (bacteria and archaea), eukaryotes have a nucleus, specialized organelles (such as mitochondria), and a sophisticated cellular organization. This complexity allowed the emergence of plants, animals, fungi, and all multicellular life.
Eukaryotes probably resulted from an endosymbiosis between an archaeon and a bacterium, giving rise to mitochondria. This symbiosis enabled the development of more complex and larger cells.
The molecular clock is a hypothesis that genetic mutations accumulate at a relatively constant rate in the genome over time. This concept, proposed in the 1960s by Zuckerkandl and Pauling, allows dating the divergence between species by comparing their DNA or protein sequences.
N.B.:
The more different the genetic sequences of two species are, the older their common ancestor, and vice versa.
Source: Nature Microbiology - The nature of the last universal common ancestor and Science - Asgard archaea illuminate the origin of eukaryotic cellular complexity.