Bayes' formula, also called Bayes' theorem, is a mathematical formula that allows you to calculate the probability of an event A, knowing that another event B has already occurred.
Bayes' formula: P(A|B) = (P(B|A) * P(A)) / P(B)
A is the event whose probability we want to estimate.
B is the event that we already know.
P(A|B) is the probability that event A will occur given that event B has already occurred.
P(B|A) is the probability that event B will occur given that event A has already occurred.
P(A) is the probability that event A occurs independently of event B.
P(B) is the probability that event B occurs independently of event A.
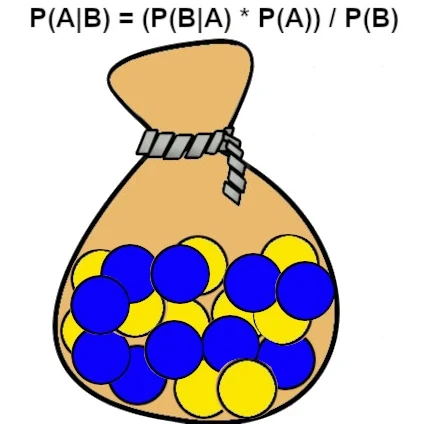
Suppose you have a bag containing 10 yellow balls and 10 blue balls. You draw a ball at random without looking and see that it is yellow.
What is the probability that the next ball you draw will also be yellow?
A: The next ball drawn is yellow.
B: The first ball drawn is yellow.
P(A|B) = (P(B|A) * P(A)) / P(B)
P(B|A) = 10/20 = 0.5 (probability of drawing a yellow ball knowing that the first ball drawn is yellow)
P(A) = 10/20 = 0.5 (probability of drawing a yellow ball)
P(B) = 10/20 + 10/20 = 1 (probability of drawing a yellow ball + probability of drawing a blue ball)
P(A|B) = (0.5 * 0.5) / 1 = 0.25
So the probability of drawing a second yellow ball is 25%.
The Bayes Formula, developed by the Reverend mathematician Thomas Bayes (1702-1761) is one of the fundamental concepts of probability theory and statistical inference (set of techniques for drawing conclusions about a population from 'a sample of this population).
What's amazing about this formula is that it allows us to change our minds based on the new information we receive. Although the formula is simple, it shows how our ideas can evolve as we learn new things. In other words, the more we know about the past, the better we can predict the future.
This formula also tells us that the accumulation of information allows us to refine our predictions. It is therefore a powerful decision-making tool.
Although born in a different context, it today finds its full meaning in the field of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
In 1763, Richard Price (1723-1791) a friend of Thomas Bayes presented his formula in an article entitled "An Essay towards solving a Problem in the Doctrine of Chances".
The notion of subjective probability, which is at the heart of Bayes' formula, was controversial at the time. Bayes did not provide a formal proof of his formula, leading mathematicians to reject it as non-rigorous.
Later, it was the work of Pierre Simon Laplace (1749-1827), Siméon Denis Poisson (1781-1840) and other mathematicians who helped solidify the foundations of probability theory and render Bayes' formula more modern. Today, the Bayes Formula is widely used in fields such as medicine, finance, and engineering.
Artificial Intelligence are computer systems capable of imitating certain human cognitive abilities.
Machine learning and probabilistic inference are two areas of AI that make particular use of Bayes' theorem.
In the context of machine learning, the Bayes Formula is used in supervised learning methods to estimate the probability that a certain class is the cause of a given observation. For example, in image classification, a machine learning algorithm can use the Bayes Formula to estimate the probability that a given image is a cat rather than a dog, based on the features observed in the image. picture.
Additionally, the Bayes Formula is at the heart of Bayesian inference, a probabilistic approach to decision-making in AI systems. Unlike the frequentist approach which is based on fixed training data, Bayesian inference updates its probabilistic beliefs as it observes new data. This enables more adaptive and robust decision-making, especially in complex and dynamic environments.
The Bayes Formula, designed over 250 years ago, is a method for learning from the uncertainty of the future. Indeed, it measures belief, it tells us that we can learn from missing data or approximations or even from total ignorance.
It therefore goes against the belief that science requires objectivity and precision. This explains why this formula was declared dead by scientists of the time.
This theory of probability, which did not want to die, with the arrival of computers has been widely demonstrated. This is the only logic of artificial intelligence algorithms. The Bayes Formula remains a powerful tool in various fields of science and technology. By combining sound statistical principles with sophisticated computer algorithms, the Bayes Formula continues to play a vital role in building intelligent and adaptive AI systems.