
On Earth, water is the only substance found naturally in its three fundamental physical states: solid (ice), liquid (water), and gas (vapor). This triple coexistence is made possible by very specific temperature and pressure conditions, which correspond precisely to those found on the surface of our planet. This phenomenon is of crucial importance in the water cycle, climate, geology, biology, and even in terrestrial thermal regulation.
The water molecule (H2O) is polar and forms hydrogen bonds between molecules. These bonds, although weak (5 to 10 times weaker than covalent bonds), stabilize the liquid phase over a wide range of temperatures (0 °C to 100 °C at atmospheric pressure). Moreover, water has a high latent heat of fusion and vaporization, which favors state changes by absorbing or releasing large amounts of energy without an immediate change in temperature.
The phase diagram of water shows that at 1 atm (average atmospheric pressure at sea level), the three states coexist between 0 °C (melting) and 100 °C (boiling).
The triple point, at 0.01 °C and 611.657 Pa, is the exact condition where the three phases coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium. Few substances exhibit such behavior under the surface conditions of a planet.
The critical point of water is a fundamental thermodynamic limit beyond which it becomes impossible to distinguish liquid water from its vapor, even by changing pressure or temperature. It is a singularity in the phase diagram of water, where the liquid-gas transition line ends.
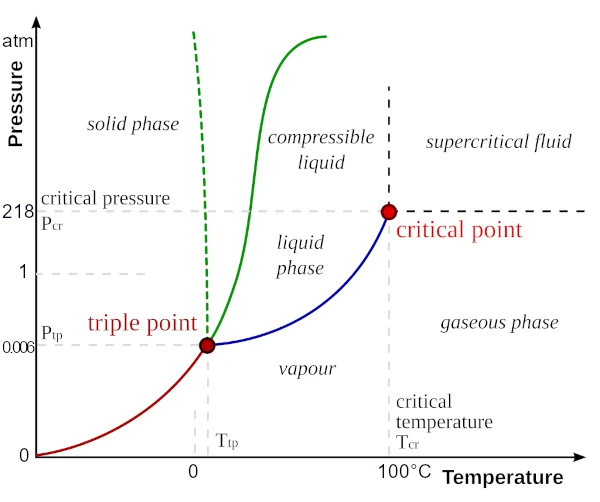
Liquid water is stable between 0 °C and 100 °C, a range that miraculously coincides with the average terrestrial temperature (about 15 °C). This "coincidence" is actually the result of a long cosmic evolution: ideal distance from the Earth to the Sun, regulating atmosphere, stable pressure, protective magnetosphere, plate tectonics recycling the oceans, etc. Other planets, like Venus or Mars, do not meet these conditions.
| State | Transition Temperature (°C) | Transition Energy (kJ/mol) | Pressure Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid → Liquid (fusion) | 0 | 6.01 | 1 atm |
| Liquid → Gas (vaporization) | 100 | 40.65 | 1 atm |
| Solid → Gas (sublimation) | -78 to 0 | 46.66 | Very low pressure |
| Triple Point | 0.01 | - | 611.657 Pa |
Sources: NIST – National Institute of Standards and Technology, USGS – Water Science School
The Earth contains a total amount of water estimated at about 1.386 billion km³. This quantity has remained almost constant since the end of the late heavy bombardment 4.4 billion years ago. It is mainly distributed in liquid form in the oceans, but also in solid form in the ice caps, and in gaseous form in the atmosphere.
The vast majority, about 97.5%, is salt water contained in the oceans. Fresh water represents only 2.5% of the total, of which nearly 70% is trapped in glaciers or polar ice caps (Antarctica and Greenland). Atmospheric water, although tiny in volume, plays a major thermodynamic role in climate regulation.
| Reservoir | Volume (km³) | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Oceans | 1,338,000,000 | 96.5% |
| Polar Ice Caps and Glaciers | 24,000,000 | 1.74% |
| Groundwater | 23,400,000 | 1.7% |
| Freshwater Lakes | 91,000 | 0.007% |
| Atmosphere | 12,900 | 0.001% |
| Water in Living Beings | 1,120 | ~0.0001% |
Sources: USGS – Water Science School, UNESCO – World Water Day.
A water molecule on Earth never remains static. Through the effect of solar radiation, it can leave an ice cap by sublimation or melting, join the ocean, then evaporate, become vapor, and form a cloud by condensation. Carried by the winds, it falls back as rain or snow and begins its cycle again. This water cycle is based on physical state changes (melting, evaporation, condensation, precipitation, solidification) governed by thermodynamic equilibria and the conservation of energy.
Each state transition is accompanied by a specific energy exchange: vaporization consumes energy (latent heat), condensation releases it. Thus, water transports not only mass but also latent thermal energy on a large scale, participating in the thermal regulation of the planet. These processes play a central role in atmospheric dynamics and global climate balances.
The water cycle feeds precipitation, recharges aquifers, irrigates soils, circulates nutrients, and feeds rivers. By shaping the terrestrial geography (erosion, sediment transport) and supporting terrestrial and aquatic biospheres, it constitutes a true planetary hydrological machine. Water thus connects the oceans, atmosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere in a coherent energy loop.