Earth's orbit around the Sun is often depicted as a circle, but it is actually a slightly flattened ellipse, characterized by an eccentricity denoted as \(e\). This eccentricity measures the degree of flattening of the ellipse: \(e = \sqrt{1 - \frac{b^2}{a^2}}\), where \(a\) is the semi-major axis and \(b\) is the semi-minor axis.
The eccentricity of Earth's orbit is not constant. It oscillates between 0.005 and 0.058 over cycles of about 100,000 years. These variations are caused by the gravitational perturbations exerted by the giant planets, notably Jupiter and Saturn, which slowly modify the shape of Earth's orbit.
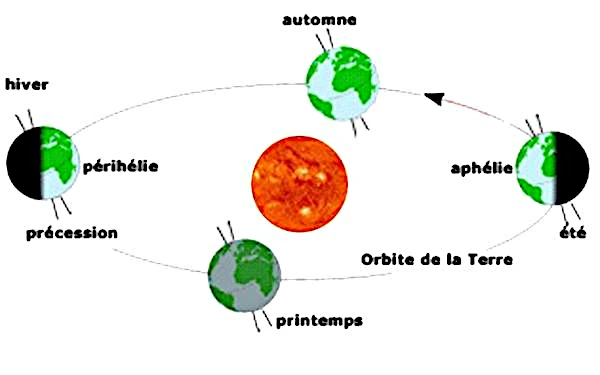
Currently, Earth follows an orbit with an eccentricity of about 0.0167, which may seem close to a perfect circle. However, this small value results in a distance difference of about 5 million kilometers between the perihelion (147.1 million km) and the aphelion (152.1 million km).
N.B.:
The aphelion is the point in the orbit where Earth is farthest from the Sun (~152.1 million km currently). At this position, the solar energy received is minimal.
N.B.:
The perihelion is the point in the orbit where Earth is closest to the Sun (~147.1 million km currently). Solar irradiance is at its maximum, which can slightly modulate the seasons, especially in the southern hemisphere currently.
This variation in distance results in a difference of about 6.7% in the solar energy received between the closest and farthest points from the Sun. Alone, this variation might seem minor, but it acts in synergy with other orbital parameters (obliquity and precession) and with Earth's feedback mechanisms (ice, albedo, CO₂, water vapor, biosphere). These combined effects are the origin of the Milankovitch climate cycles, which explain the glacial/interglacial alternations observed over the last few million years.
Variations in eccentricity influence the average distance between Earth and the Sun, thus modifying the received insolation. During periods of maximum eccentricity, the difference between perihelion and aphelion becomes significant. Combined with other orbital parameters (obliquity and precession), this variation is the origin of the Milankovitch cycles that pace the ice ages.
| Planet | Eccentricity | Orbit Type | Climatic Consequences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mercury | 0.2056 | Highly elliptical | Very large thermal amplitudes |
| Venus | 0.0068 | Very circular | Climate little influenced by orbit |
| Earth | 0.0167 | Almost circular | Indirect but major impact on long-term climate |
| Mars | 0.0934 | Markedly elliptical | Large seasonal variations |
| Jupiter | 0.0489 | Slightly elliptical | Dominant internal climatic effects |
| Saturn | 0.0565 | Moderately elliptical | Moderate effects, thick atmosphere |
| Uranus | 0.0457 | Slightly elliptical | Climate dominated by extreme tilt |
| Neptune | 0.0113 | Very circular | Negligible variations |
Source: NASA – Planetary Fact Sheet
Even if the eccentricity of Earth's orbit seems small, its consequences on the global climate are notable on geological time scales. Combined with other orbital parameters, it shapes the major climatic trends of our planet and plays a key role in the alternation of glacial and interglacial periods.
Here are the main climatic cycles identified over the last 800,000 years:
| Period | Type | Approximate Duration | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 to 11,700 years ago | Interglacial (Holocene) | 11,700 years | Stable and warm climate, current period |
| 11,700 to 115,000 years ago | Glacial (Würm/Wisconsin) | 103,000 years | Last glacial maximum around 21,000 years ago |
| 115,000 to 130,000 years ago | Interglacial (Eemian) | ~15,000 years | Temperatures higher than those of the Holocene |
| 130,000 to 190,000 years ago | Glacial | ~60,000 years | Cycle marked by decreasing obliquity |
| 190,000 to 240,000 years ago | Interglacial | ~50,000 years | Relatively stable |
| 240,000 to 330,000 years ago | Glacial | ~90,000 years | Triggered by low eccentricity + unfavorable precession |
| 330,000 to 400,000 years ago | Interglacial (MIS 11) | ~70,000 years | Exceptionally long and warm period |
Data from: EPICA Dome C, Vostok Ice Core (Petit et al., 1999; Jouzel et al., 2007), LR04 (Lisiecki & Raymo, 2005).