The Earth, like any rotating object, possesses angular momentum, which is the product of its moment of inertia I and its angular velocity ω (the speed of the Earth's rotation around its axis). The moment of inertia depends on the distribution of the Earth's mass relative to its axis of rotation.
I=∫r2 dm (r is the distance of a mass element dm from the axis of rotation).
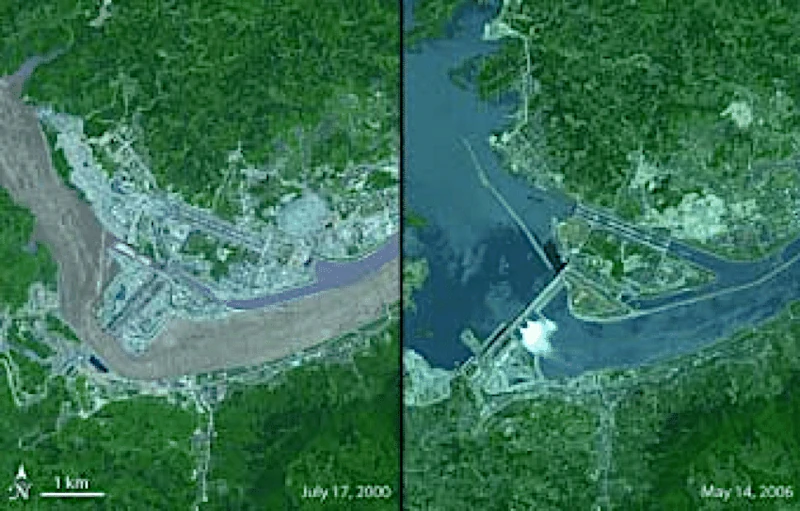
The Three Gorges Dam has an enormous water storage capacity, approximately 39.3 billion cubic meters. When this mass of water is stored, it is located at a higher altitude than the average surface of the Earth in that region. When this water is moved from the river (at a lower level) to the reservoir (at a higher level), it changes the distribution of the Earth's mass.
By storing a large quantity of water at a higher altitude, the Earth's moment of inertia increases. Indeed, the farther the mass is from the axis of rotation, the more it contributes to increasing the moment of inertia. According to the principle of conservation of angular momentum, if the moment of inertia I increases and the angular momentum L remains constant (since there is no major external force acting on the Earth system as a whole), the angular velocity ω must decrease.
L = I x ω = constant
Thus, if I increases, ω must decrease.
A decrease in the Earth's angular velocity means that the Earth takes slightly longer to complete a rotation, resulting in a very minimal increase in the length of the day.
The effect of the Three Gorges Dam on the length of the day is extremely small. According to estimates, the dam has lengthened the day by the order of microseconds (10⁻⁶ seconds). Although this is a real effect, it is so minimal that it has virtually no impact on daily life.
• Very powerful earthquakes can alter the distribution of Earth's mass.
• Large-scale extraction of oil, gas, or other minerals can redistribute Earth's internal masses.
• Large-scale extraction of oil, gas, or other minerals can redistribute Earth's internal masses.
• The melting of large ice masses due to climate change redistributes water from the poles to the oceans.
• Earth's tides, caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon, affect Earth's rotation.
• Convective currents and other movements in the Earth's mantle can shift large internal masses, slightly altering Earth's moment of inertia.
• Isostatic adjustments, such as the post-glacial rebound of land after the melting of polar ice caps, change mass distribution and can affect Earth's rotation.
In addition to the 13 cities and 1,350 villages, about 162 archaeological sites were submerged, and more than 1.3 million people had to be relocated. The project was one of the largest population relocation operations in modern history.
The slowing of Earth's rotation caused by the Three Gorges Dam is due to the increase in Earth's moment of inertia, brought about by the retention of a large mass of water at a higher altitude.
This change dramatically illustrates how large-scale human actions can influence the physical properties of our planet.