The thermonuclear reactions that occur inside the Sun release enormous amounts of energy. Most of this energy is released into nearby space in the form of electromagnetic radiation, primarily visible light.
The Sun also emits a flux of charged particles called the Solar Wind. The solar wind is bimodal, a mixture of several types of winds, fast (3 million km/h) at high solar latitudes above 40°, and slow (1 million km/h) at latitudes between 22°S and 21°N. The solar wind is ionized, with electrons and protons separated, forming a plasma that travels to the far reaches of the solar system.
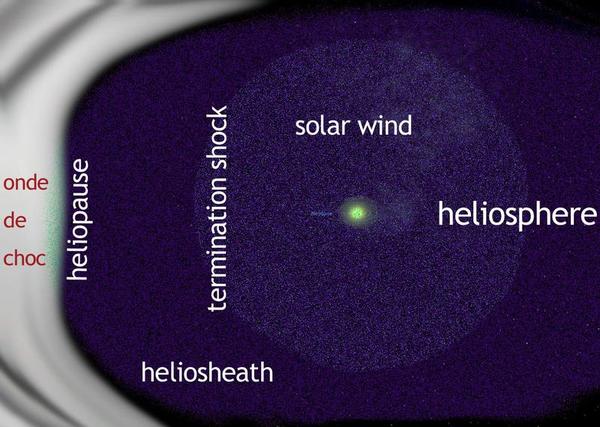
The Heliopause is the final frontier of the solar system, located at approximately 130 AU (20 billion km), where the solar wind fades and interstellar space begins.
At this point, the solar wind collides with opposing winds from the interstellar medium. Its push is no longer sufficient to repel the rarefied hydrogen and helium of the Galaxy.
The distance to the heliopause is not precisely known because it likely varies depending on the speed of the solar wind and the temporal density of the interstellar medium. In this region, known as the "magnetic highway," the instruments on the Voyager 1 probe recorded the highest rate of cosmic rays from interstellar space and a sharp decrease in particles from the Sun.
The Termination Shock is an intermediate boundary located before the heliopause. This region between the termination shock and the heliopause is called the Heliosheath.
The heliosheath is the turbulent zone where the solar wind is slowed and then compressed by interstellar pressure. When particles emitted by the Sun (a few particles per cubic centimeter) collide with interstellar particles, they slow down, heat up, and emit energy. These highly energized particles accumulate in front of the heliopause and create a shock wave. This shock wave is a trace left by the Sun during its journey through the Milky Way, which it traverses in approximately 220 million years.
N.B.:
The three units of measurement in astronomy for expressing distances.