A near-Earth asteroid (or NEA for Near-Earth Asteroid) is an object whose orbit approaches within 1.3 astronomical units (AU) of the Sun, meaning within 195 million kilometers. This means it can potentially come dangerously close to Earth. Near-Earth asteroids are divided into orbital subclasses (Apollo, Amor, Atira, Aten) based on the shape and location of their orbit, but their composition is a separate classification.
| Type | Semi-major axis (a) | Perihelion (q) | Aphelion (Q) | Main characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atira (or Apohele) | < 1 AU | > 0.983 AU | < 1 AU | Orbits entirely within Earth's orbit |
| Aten | < 1 AU | < 1.017 AU | > 1 AU | Mostly interior orbits, but cross Earth's orbit |
| Apollo | > 1 AU | < 1.017 AU | > 1 AU | Mostly exterior orbits, also cross Earth's orbit |
| Amor | > 1 AU | between 1.017 and 1.3 AU | - | Approach Earth's orbit without crossing it |
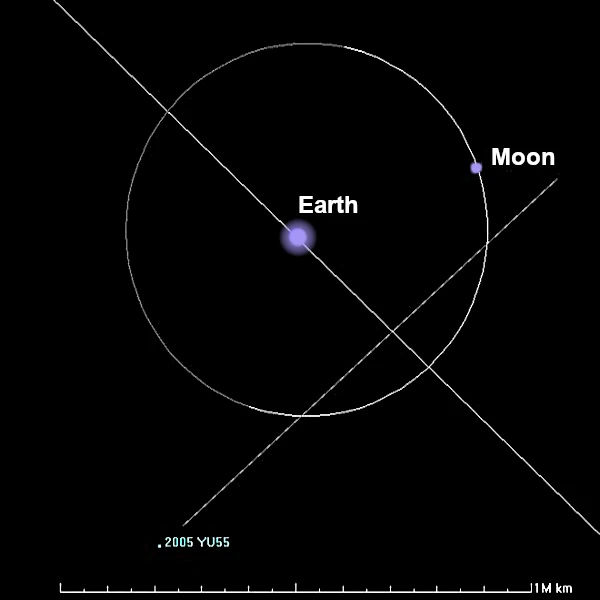
On November 8, 2011, Asteroid 2005 YU55 passed just 324,600 km from Earth, a distance less than that separating our planet from the Moon (384,400 km). This object, with a 400-meter diameter, belongs to the class of near-Earth C-type asteroids (dark, carbon-rich), and represents one of the largest celestial objects to have come so close to Earth since radar observation has allowed tracking these bodies. This event, known as a flyby, posed no immediate danger but allowed an exceptional observation campaign led by NASA, notably via the radar antennas at Goldstone and Arecibo.
2005 YU55 is a dark asteroid, with an albedo of only 0.06, typical of carbon-rich objects (C spectral type). Its shape is almost spherical, and its rotation is relatively slow with a period of 18 hours. According to radar data, it consists of primitive carbonaceous materials, similar to those found in some chondritic meteorites. Spectral analysis indicates a mixed rocky composition, potentially rich in volatile compounds, making it an excellent candidate for a future robotic or manned exploration mission.
The asteroid 2005 YU55 is classified as a PHA (Potentially Hazardous Asteroid), but orbital ephemerides show no significant probability of collision at least until 2136 (CNEOS/NASA). An inclination of 0.4° relative to the ecliptic plane is very low, meaning the two orbital planes are almost coincident. The trajectory of 2005 YU55 necessarily crosses the ecliptic plane twice per orbit (ascending node and descending node).
The approach of 2005 YU55 allowed for high-resolution radar measurements, enabling the reconstruction of its topography and estimation of its surface properties. The combination of radar technologies, space telescopes, and orbital calculations now ensures effective planetary monitoring. Although 2005 YU55 continued on its course without consequence, it reminds us of our planet's vulnerability to wandering cosmic bodies. Nevertheless, this approach highlighted the need for space surveillance programs such as NEO-WISE or Pan-STARRS, to anticipate potential impacts from similarly sized objects.