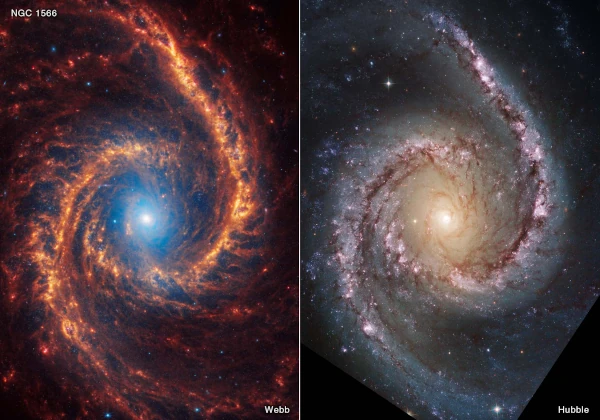
A galaxy is a gigantic cosmic structure composed of billions of stars, planets, gases, dust, dark matter, and black holes. Each galaxy is a complex system where these elements interact under the influence of gravity.
Galaxies appeared about 13 to 13.5 billion years ago, shortly after the formation of the first stars. Their evolution has been shaped by complex processes, including the merging of galaxies, star formation, and the influence of dark matter.
Stars are the most visible components of a galaxy. They are born in clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. Stars vary in size, mass, and temperature, ranging from red dwarfs to blue giants. Their life cycle, from birth to death, influences the dynamics of the galaxy.
Many stars have orbiting planets, forming planetary systems. These planets can be rocky, like Earth, or gaseous, like Jupiter. Some may harbor life, making galaxies potential sites for the search for extraterrestrial life.
Interstellar gas, mainly hydrogen and helium, fills the space between stars. This gas is crucial for the formation of new stars. When it condenses under the effect of gravity, it gives birth to stellar nurseries.
Interstellar dust is composed of tiny solid particles. It plays a key role in the formation of stars and planets by absorbing and re-emitting light, influencing the temperature and chemistry of molecular clouds.
Dark matter is a mysterious substance that neither emits nor absorbs light but whose presence is inferred from its gravitational effects. It accounts for about 85% of the total matter in a galaxy and is essential for explaining the rotation of galaxies.
At the center of many galaxies lies a supermassive black hole. These extremely dense objects exert such a strong gravitational pull that not even light can escape. They play a key role in the evolution of galaxies.