The apsides refer to the extreme points of an elliptical orbit. The closest point to the gravitational focus is called the periapsis (or perihelion in the case of the Sun), while the farthest is the apoapsis (or aphelion). In planetary orbits, these points are crucial for understanding orbital dynamics, as they directly depend on the eccentricity \( e \) and the major axis \( 2a \) of the ellipse. The distances are given by: $$ r_{\text{min}} = a(1 - e),\quad r_{\text{max}} = a(1 + e) $$ where \( a \) is the semi-major axis. These formulas show that the greater the eccentricity, the more elongated the orbit, and the greater the difference between perihelion and aphelion.
The interest of apsides also lies in their temporal mobility: under the effect of gravitational perturbations, particularly interplanetary ones, the apsidal lines (the line joining perihelion and aphelion) can precess, that is, slowly rotate in the orbital plane. This precession is a sensitive indicator of non-Newtonian effects, as shown by the advance of Mercury's perihelion explained by general relativity.
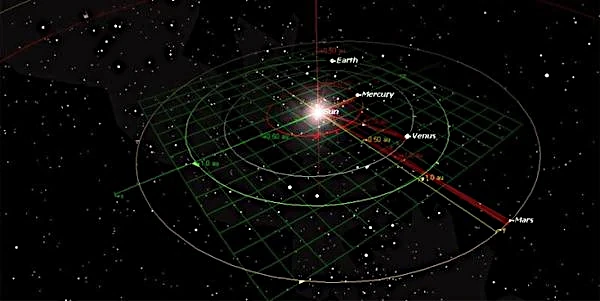
The inner planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars) have orbits relatively close to the Sun, which intensifies tidal effects and interactions with the solar wind. Their apsides are measured with great precision thanks to modern ephemerides. Mercury, with its high eccentricity \( e \approx 0.206 \), has a very elliptical orbit: its perihelion is at 46 million km, and its aphelion at 70 million km. This imbalance results in a highly variable orbital speed, ranging from 59 km/s near the Sun to about 39 km/s at aphelion.
The precession of Mercury's perihelion is an emblematic phenomenon. While Newton's laws predict a certain advance due to perturbations from other planets, observations show an excess of 43" (arc seconds) per century, perfectly explained by the curvature of spacetime in Einstein's formalism.
Earth, with an almost circular orbit \( e \approx 0.0167 \), shows a modest variation between perihelion (147.1 million km) and aphelion (152.1 million km). This difference influences the amount of solar energy received (the solar constant varying by ~6%) but is not the main cause of the seasons, which depend on the axial tilt of 23.5°.
Mars, being farther away, has an eccentricity of 0.093, almost six times that of Earth. Its perihelion (206 million km) and aphelion (249 million km) show much more pronounced seasonal variability, particularly visible in its asymmetric climate between hemispheres.
Venus is an interesting case: its orbit is almost perfectly circular \( e \approx 0.0068 \). As a result, the variation between its apsides is negligible, but it plays an important role in the transits observed from Earth when the alignments are exact at the node passage.
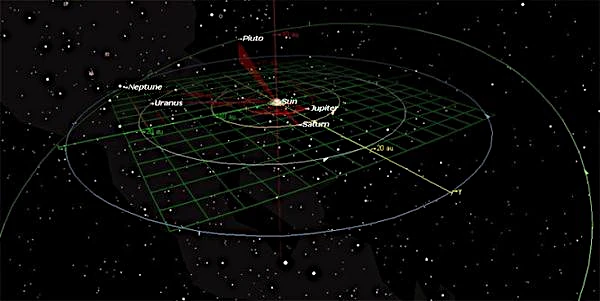
The outer planets (Jupiter to Neptune) describe larger and generally more circular orbits than those of the inner planets. Nevertheless, they undergo mutual gravitational resonances that slowly modify their apsides. Jupiter, the dominant giant, strongly influences the architecture of the solar system. Its perihelion is at 740 million km, and its aphelion at 816 million km, with a moderate eccentricity \( e \approx 0.049 \).
Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune have relatively small apsidal differences (a few tens of millions of km) compared to their average distances, making their motion more stable over the long term. However, their orbits are also subject to a slow precession of their apsidal lines, detected by spectroscopic analysis of the rings or satellite tracking.
Trans-Neptunian bodies show more extreme eccentricities. Pluto, with \( e \approx 0.2488 \), ranges from 4.4 billion to 7.3 billion km depending on whether it is at perihelion or aphelion. This variation is such that Pluto can temporarily be closer to the Sun than Neptune. Its apsidal line is inclined (~17°) and highly mobile, reflecting a chaotic regime.
Other distant objects like Eris, Sedna, or the extreme objects of the Oort cloud, reach aphelia greater than 500 AU. Sedna, for example, has a highly eccentric orbit \( e \approx 0.854 \), with a perihelion at 76 AU and an aphelion estimated at 937 AU. These objects are fossil witnesses of past perturbations, perhaps linked to nearby stars or a hypothetical planet not yet detected.
These distant apsides are essential for understanding the boundaries of the solar system and the gravitational forces that reign there. They are studied by numerical simulation, as their trajectory cannot be described in a simple analytical way, especially when relativistic effects, resonances, and galactic tides are taken into account.