
Our Universe is truly vast and empty, yet a few grains of matter are scattered throughout this cosmic void, from tiny dust particles to the largest stars. The size difference between the smallest planets in the solar system and the largest stars is enormous. For example, the diameter of the star Betelgeuse is 141,863 times larger than Earth's diameter. This page shows some size comparisons between planets and stars. In the solar system, the Sun captured 99.86% of the total mass of dust and gas from the original nebula.
Jupiter, the largest planet in the system, captured 71% of the remainder. The other planets shared the residual mass from this gravitational evolution, which is 0.038% of the total mass. The 4 terrestrial planets represent only ≈ 11% of the total mass of the planets in the solar system.
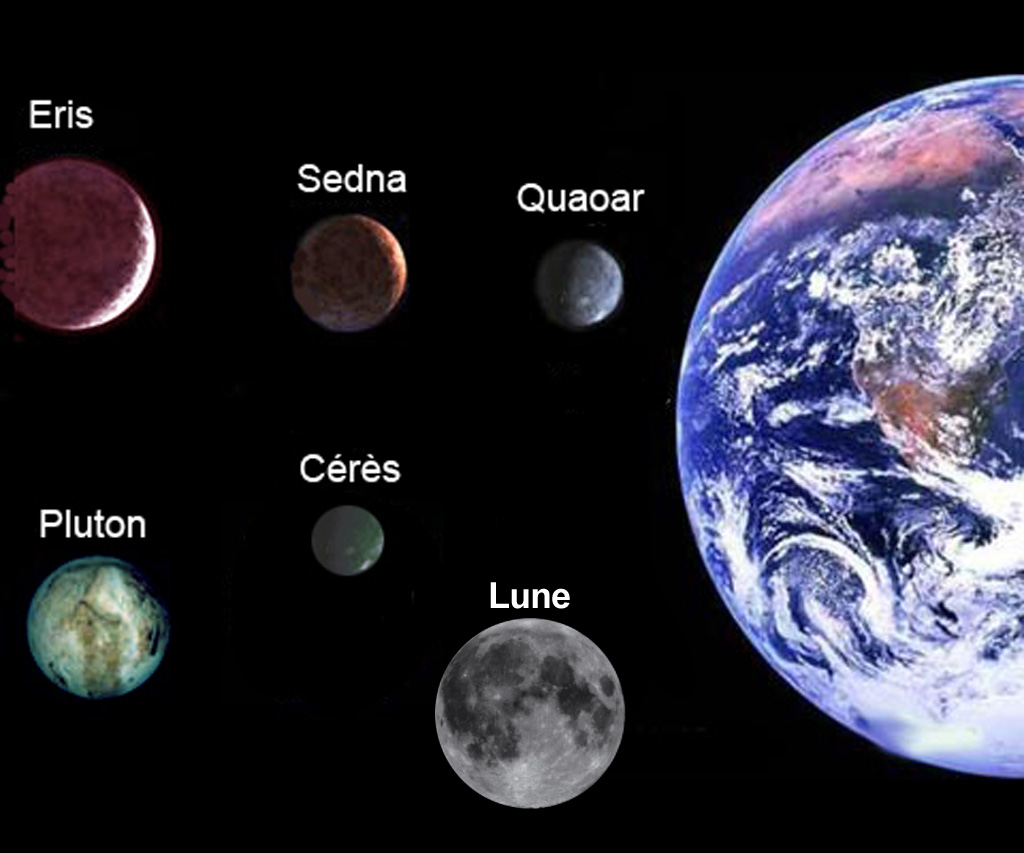

A dwarf planet, according to the new definition from August 2006, is a celestial body orbiting the Sun that has sufficient mass for its gravity to overcome the rigid body forces and maintain hydrostatic equilibrium (in an almost spherical shape), and is not a satellite, but has not cleared its orbit of other debris.

In 1879, the Austrian physicist Josef Stefan (1835-1893), who was interested in the radiation of hot bodies, discovered that the total energy emitted by an object is proportional to the fourth power of its absolute temperature.
Thanks to the Stefan-Boltzmann law, astronomers can calculate the radii of stars. The luminosity L of a star is given by: L = 4πσR²T⁴. L is the luminosity, σ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant, R is the radius of the star, and T is its temperature.
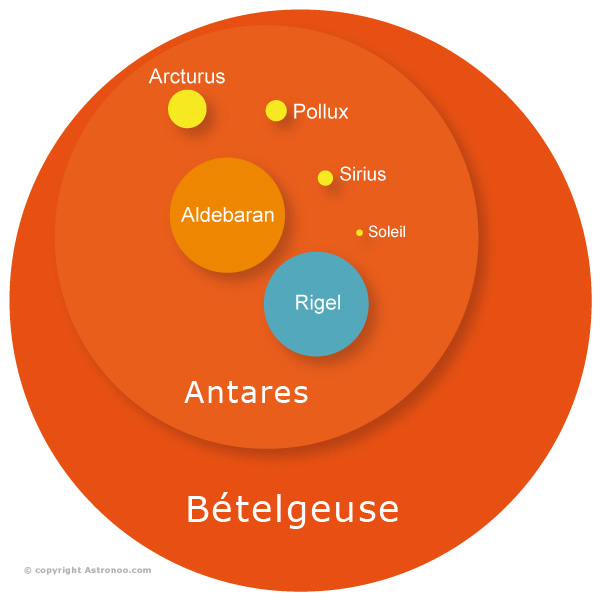
Our Sun is truly tiny compared to some stars. Planets are mere specks compared to the blue and red giants in our Universe.
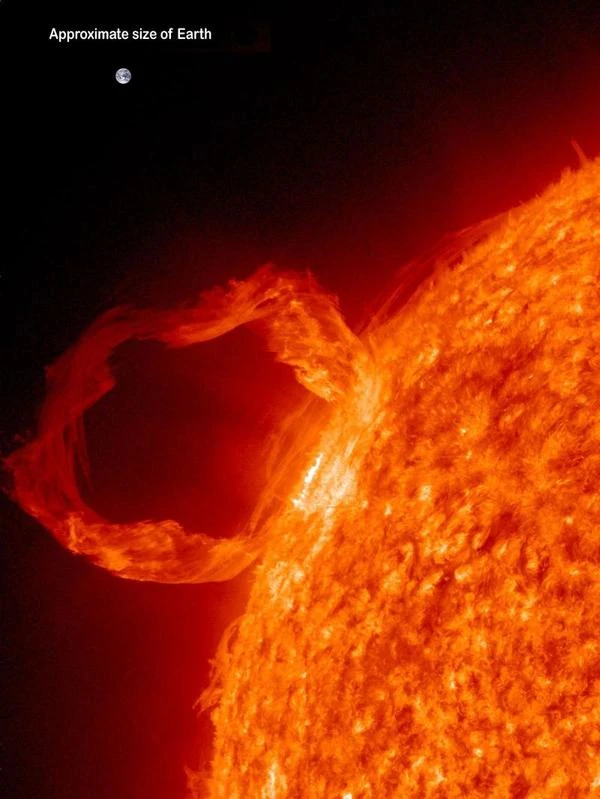

Earth is quite small compared to the Sun. The Sun's volume could contain more than a million Earths (1,305,620). Its average diameter is ≈ 12,742 km, while the Sun's diameter is ≈ 1,392,684 km (≈ 109 times larger). The image shows this size ratio of Earth to the Sun if Earth were on the same plane, very close to the Sun.
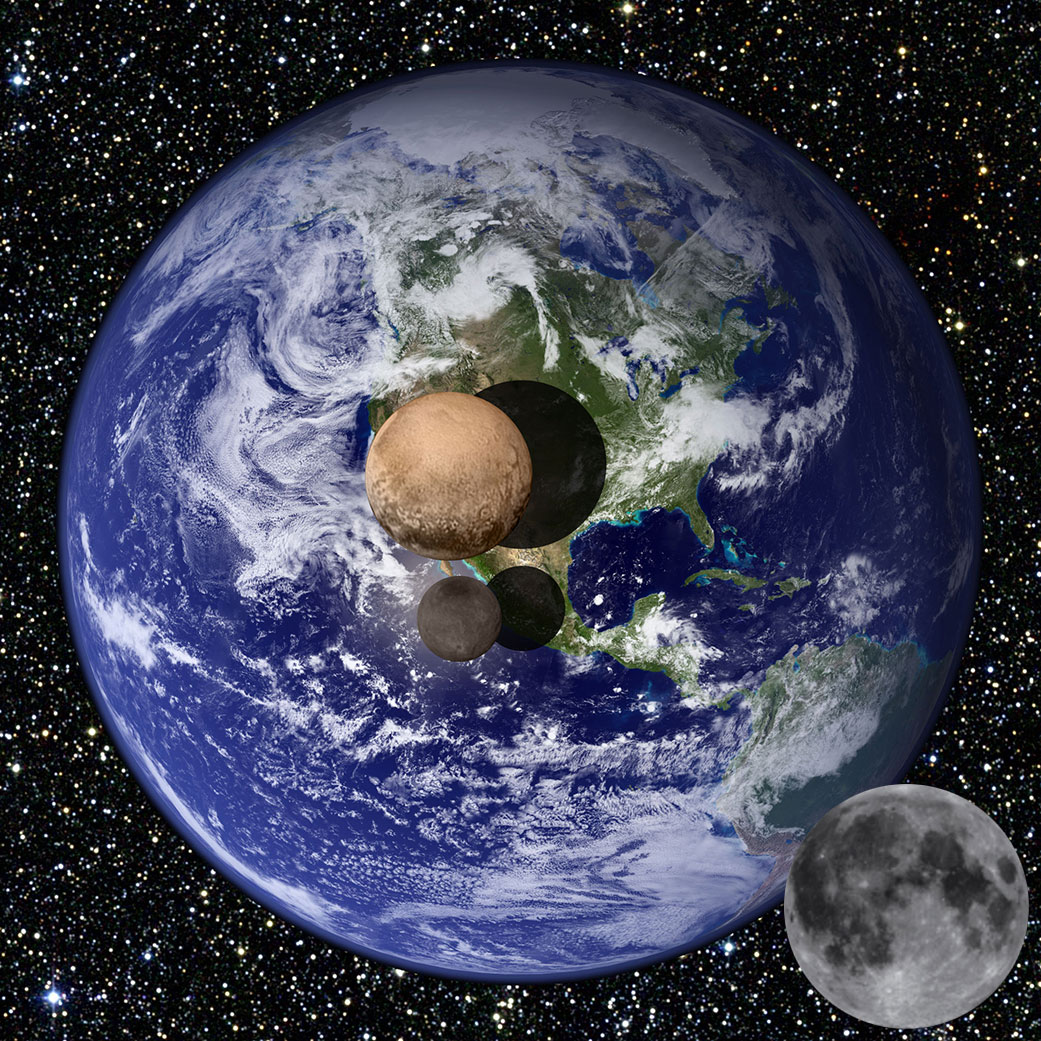

The new measurements and images of Pluto and Charon obtained by the New Horizons probe (July 2015) allow us to create this comparative montage. This graphic shows a view of Pluto (center of the image) and Charon (the small object below Pluto). Pluto has a diameter of 2370 km (18.5% of Earth's diameter), while Charon has a diameter of 1208 km (9.5% of Earth's diameter). The dwarf planet Pluto is smaller than our Moon (bottom right of the image) with a diameter of 3575 km (27.3% of Earth's diameter).