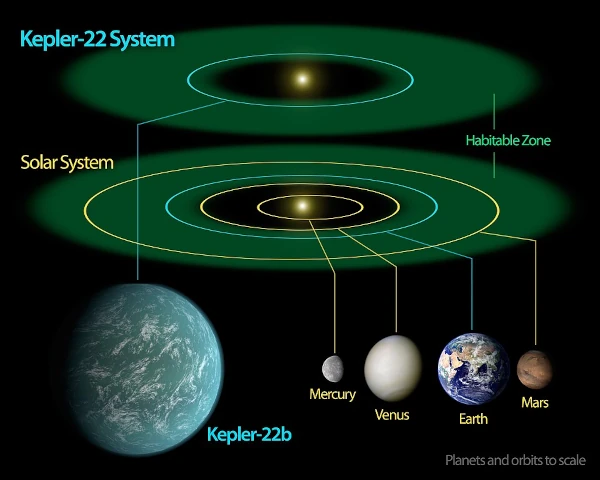
Discovered in 2011 by the Kepler space telescope, Kepler-22b is a super-Earth type exoplanet located about 600 light-years away in the constellation Cygnus. It is particularly notable because it orbits in the habitable zone of its star, a G5 spectral type yellow dwarf, similar to our Sun but slightly cooler and smaller.
The planet completes a full revolution in 289 days, at a distance of about 0.85 AU (astronomical units) from its star, which theoretically allows water to exist in liquid form, an essential condition for life as we know it. Its terrestrial thermal equivalent is estimated at 22°C, assuming an atmosphere similar to that of Earth.
With a radius 2.4 times that of Earth, Kepler-22b is classified among the super-Earths, a type of exoplanet intermediate between Earth and Neptune. Its exact mass is not known, but models suggest it could be composed of a mixture of silicates, water, and possibly a thick atmosphere. Its density, not yet directly measured, will condition the formation scenarios and habitability hypotheses.
The Kepler mission, based on the transit method, detected Kepler-22b by observing periodic drops in the brightness of the host star. The depth of the transit (around 500 ppm) and its periodicity allowed the deduction of its radius and orbital period. Further observations, particularly spectroscopic ones, will be necessary to estimate its mass and characterize its atmosphere (if it has one).
The scientific interest in Kepler-22b is immense, as it is the first intermediate-sized exoplanet discovered in the habitable zone of a solar-type star. This paves the way for research on the frequency of potentially habitable planets in our galaxy.
The detection of Kepler-22b was largely a stroke of orbital and temporal luck. Indeed, the transit method used by the Kepler telescope relies on a very strict condition: the planet's orbit must be almost perfectly aligned with our line of sight from Earth. This geometric criterion significantly reduces the probability of observing a transit for a given star.
For an orbit at 0.85 AU, the admissible alignment angle is about 0.5°, meaning that less than 1% of such systems will present a visible transit from our position. Additionally, Kepler-22b has a long orbital period (~289 days): thus, several years of continuous observations are needed to observe at least three transits necessary for confirmation.
Kepler-22b was detected after only 15 months of the mission, implying that the three transits necessary for identification were observed at the beginning of the campaign—a statistical rarity. If even one transit had been missed (due to occultation, instrumental noise, or signal loss), this planet would have gone unnoticed.
This discovery highlights how the detection of exoplanets by transit is a science of opportunity as much as precision. It also justified the need to extend long-term continuous observation missions, such as those of the TESS or PLATO telescopes.