In the confusing and turbulent world around us, there are regularities that allow us to make sense of the apparent chaos. For example, we notice that the Earth regularly orbits the Sun in one year, that days follow nights, that the nautilus builds its shell in spirals, or that the honeycomb cells of bees are hexagonal…
All civilizations have been on the lookout for these regularities, rhythms, repetitions, and patterns that amaze and reassure us. This allows us to believe that there is an order or a purpose in our observable Universe.
Throughout history, these regularities, whether contingent or accidental, have inspired philosophers, physicists, mathematicians, and especially musicians.
When we talk about regularities, we think of sounds. In music, an octave corresponds to a doubling of frequency f, 2f, 3f, etc. These multiple frequencies of a given frequency are called harmonics. For example, the note C has a frequency of 260 Hz, the next C is at 520 Hz. The note G has a frequency 1.5 times that of C, the next G is equal to 3 times C, etc. These regularities are sufficient to establish musical harmony.
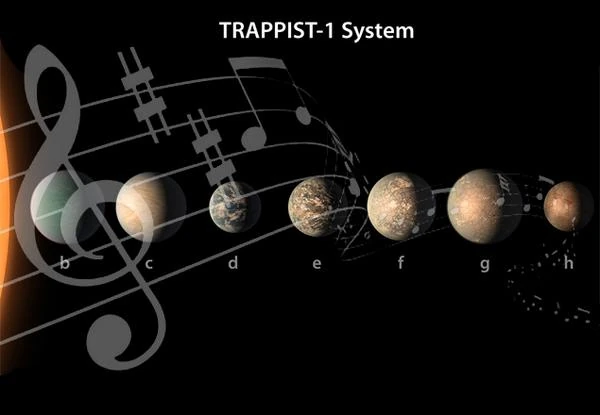
The TRAPPIST stellar system, discovered in 2016 by the transit method, is 7.6 billion years old and is located in the constellation of Aquarius, 39.5 light-years away. This system consists of an ultra-cool dwarf star called TRAPPIST-1a and at least 7 rocky planets (TRAPPIST-1b, TRAPPIST-1c, TRAPPIST-1d, TRAPPIST-1e, TRAPPIST-1f, TRAPPIST-1g, TRAPPIST-1h).
Three of them are located in the star's habitable zone, and TRAPPIST-1e has a density close to that of Earth, and it is likely to have an iron core and a liquid or frozen ocean.
Aided by a computer model, scientists have simulated the planetary orbits and discovered that the 7 planets are in perfect orbital harmony. In other words, each planet has simple ratios with the orbital periods of its neighbors. When the outermost planet TRAPPIST-1h completes 2 orbits, its neighbor TRAPPIST-1g completes 3 orbits, TRAPPIST-1f completes 4 orbits, TRAPPIST-1e completes 6 orbits, TRAPPIST-1d completes 9 orbits, TRAPPIST-1c completes 15 orbits, and TRAPPIST-1b completes 24 orbits. The entire system moves with remarkable regularity.
The planets of the TRAPPIST-1 system are therefore in perfect orbital resonance, and these harmonious orbits can be translated musically, with notes. TRAPPIST-1b corresponds to the note B (B flat in Anglo-Saxon form), TRAPPIST-1c corresponds to the note C, TRAPPIST-1d corresponds to the note D, etc.
Each planet plays a note per orbit when it passes between us and its star, and a rhythmic beat sounds each time it passes in front of its neighbor. Since each planet resonates with its neighbors, the entire system forms a chain of harmonic resonance.
This is what this dazzling and melodious animation shows (in fast motion) where the seven planets waltz in almost perfect synchrony.