The concept of a habitable planet refers to a celestial body whose physical and chemical conditions allow the emergence, development, and persistence of life as we know it. These conditions mainly include the presence of liquid water, a moderate temperature, a protective atmosphere, and energy sources. In astrophysics, this zone is often called the "habitable zone" (or Goldilocks zone) around a star, that is, the region where a planet can theoretically maintain liquid water on its surface for billions of years.
For a planet to be potentially habitable, several criteria must be met:
The Kepler, TESS, and now James-Webb missions have identified several rocky exoplanets in the habitable zone of their star. Some of them, such as Proxima b, TRAPPIST-1e, Kepler-442b, or LHS 1140b, are considered serious candidates. However, these observations do not yet allow the direct detection of biosignatures.
| Exoplanet | Mass (Earth = 1) | Radius (Earth = 1) | Distance (LY) | Habitable zone | Type of star |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proxima Centauri b | 1.27 | ~1.1 | 4.24 | Yes | Red dwarf M5.5 |
| TRAPPIST-1e | 0.77 | 0.92 | 39.6 | Yes | Ultra-cool dwarf |
| Kepler-442b | 2.36 | 1.34 | 1,206 | Yes | Orange dwarf K |
| LHS 1140b | 6.6 | 1.7 | 41 | Yes | Red dwarf M4.5 |
| Kepler-22b | ~8.7 (estimate) | 2.4 | 620 | Yes | Yellow dwarf G5 |
| Kepler-62f | ~2.8 (estimate) | 1.4 | 1,200 | Yes | K2 dwarf |
| Kepler-186f | ~1.4 (estimate) | 1.1 | 490 | Yes | M1 dwarf |
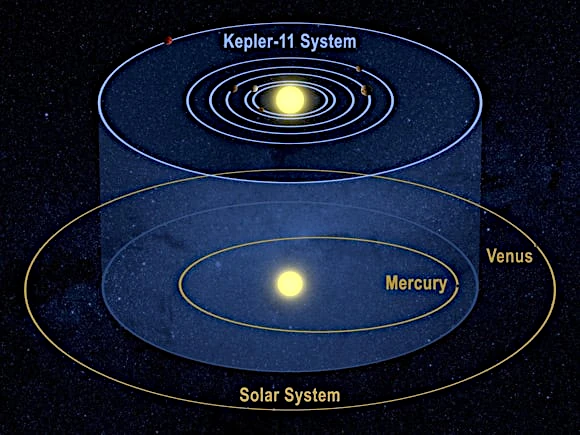
| Kepler-11f | ~2.3 | 2.6 | 2,000 (approx.) | Inner limit | Yellow dwarf G |
| Kepler-11g | ~8.0 | 3.3 | 2,000 (approx.) | Outer limit | Yellow dwarf G |
Even if the physical conditions of some exoplanets seem promising, the chemical complexity leading to life remains an open question. The emergence of life depends on many stochastic processes (effect of chance): prebiotic chemistry, self-organization, homochirality, encapsulation, and stability over time. In this context, life could be frequent in the Universe, but complex life probably remains unfindable.
Habitable planets constitute one of the most dynamic fields of modern astrophysics. They pave the way for a new era of space exploration, focused not only on celestial objects but on the search for another form of life. The development of observatories like JWST or ELT could, in the near future, allow the detection of spectroscopic biosignatures.
References:
• Kaltenegger L., How to Characterize Habitable Worlds and Signs of Life, Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2017.
• NASA Exoplanet Archive: https://exoplanetarchive.ipac.caltech.edu/
• Seager S., Exoplanet Habitability, Science, vol. 340, 2013.