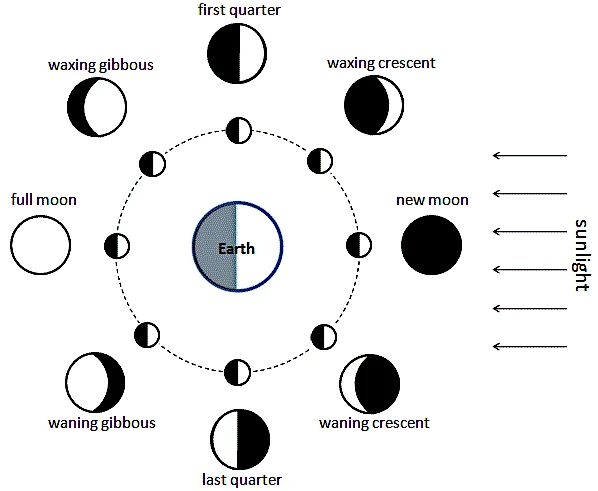
Moon phases correspond to the different appearances of the illuminated portion of the Moon visible from Earth. These variations are due to the relative positions of the Sun, Earth, and Moon. The complete cycle, called a synodic month, lasts approximately 29.5 days.
Moon phases result from the interaction between sunlight and the Moon's orbital motion around Earth. As the Moon orbits our planet, the part illuminated by the Sun changes gradually in appearance to an Earth-based observer. This mechanics is directly related to the Moon's orbital inclination relative to the ecliptic plane.
A synodic month, the time required for the Moon to go from one new moon to the next, lasts approximately 29.5 days. During this cycle, the Moon goes through the different phases, revealing the complex gravitational interactions between Earth, the Moon, and the Sun.
Observing moon phases is accessible to everyone, even without specialized equipment. However, it is preferable to choose a location away from light pollution for better visibility. Binoculars or a small telescope can reveal more details about the lunar surface.
Many astronomical applications and calendars allow you to accurately track the lunar cycle. Evenings near the first or last quarter often offer spectacular contrasts of lunar craters and mountains, thanks to the angle of sunlight.
Lunar phases influence many terrestrial phenomena. Tides, for example, result from the gravitational pull of the Moon and Sun. Full moon and new moon periods cause stronger tides, known as spring tides.
In human cultures, moon phases have inspired myths, calendars, and agricultural practices. Some traditions associate the Moon with specific animal behaviors, such as the synchronization of spawning in certain corals.
Lunar exploration missions consider the phases to optimize landing and observation conditions. For example, during the Apollo missions, NASA planned lunar landings near the first quarter to benefit from long shadows, aiding the astronauts' visual navigation.
In the future, lunar cycles will continue to play a role in permanent lunar base projects, influencing available light and solar energy cycles.
The Moon holds a central place in many mythologies around the world. Moon phases are often associated with deities, rituals, and beliefs. In Greek mythology, Selene, the goddess of the Moon, is often depicted driving a chariot illuminating the night.
In Chinese culture, the full moon symbolizes family reunion and is celebrated during the Mid-Autumn Festival. Moreover, some European legends associate the full moon with supernatural transformations, such as the werewolf myth.