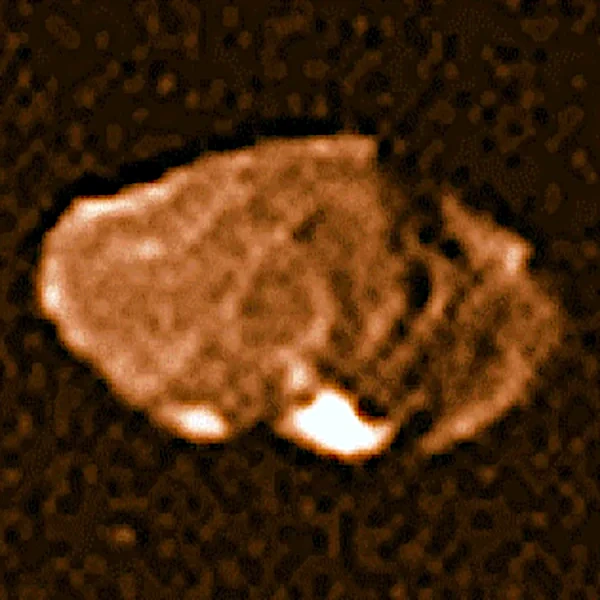
Discovered in 1892 by Edward Emerson Barnard (1857-1923), Amalthea is the third moon of Jupiter by distance and one of the most intriguing of its inner satellites. With an average radius of about 83 km, it has an irregular shape resembling a giant rock deformed by the planet's gravity. Its intense red color intrigues planetary scientists: it could be linked to sulfur compounds from Io's eruptions or a thin layer of interplanetary dust trapped on its surface.
Amalthea orbits Jupiter at a distance of about 181,000 km, or just 2.5 Jovian radii from the planet's center. It lies within Jupiter's tenuous ring system and directly contributes to their supply. Micrometeorites constantly striking its surface eject dust that integrates into the Gossamer ring. This dynamic interaction between gravity, dust, and plasma creates a complex environment where material density varies with Jovian magnetic latitude.
Measurements taken by the Galileo probe revealed that Amalthea has an average density of only 0.86 g/cm³, less than that of water. This value indicates a composition mainly of ice mixed with porous and fractured material. With a surface gravity of only \(1.8 \times 10^{-3}\) m/s², an astronaut could easily jump hundreds of meters high. This low density supports the hypothesis of a primitive origin, perhaps an icy fragment captured in the early days of the Jovian system.
Amalthea shows pronounced reliefs: Mons Pan and Gaea Crater reach several kilometers in depth. These structures indicate violent impacts and weak internal cohesion. Its orbit, very close to Jupiter, also exposes it to intense bombardment by energetic particles trapped in the planet's magnetosphere. The incident radiation causes fluctuating electrostatic charge and slow erosion of surface materials.
Despite its small size, Amalthea strongly reflects sunlight, sometimes appearing as a reddish point during Jovian occultations. Its surface, composed of irregular materials, scatters light according to a modified Rayleigh law. The light reflected by Amalthea faintly illuminates the upper layers of the inner rings, thus contributing to the diffuse luminosity observed in Jupiter's environment.
N.B.:
Jupiter's inner moons (Metis, Adrastea, Amalthea, and Thebe) all orbit within the Jovian magnetosphere. Their interaction with coronal plasma generates luminous arcs and radio emissions detectable from Earth.
| Parameter | Average value | Unit | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean radius | 83.5 | km | Irregular shape, very elongated (250 × 146 × 128 km) |
| Mass | 2.08 × 1018 | kg | Low gravity, close to \(1.8 \times 10^{-3}\) m/s² |
| Density | 0.86 | g/cm³ | Indicates a porous structure composed of ice and silicates |
| Average distance from Jupiter | 181,366 | km | Located in the inner Gossamer ring |
| Orbital period | 0.498 | Earth days | Synchronized orbits, rotation locked on Jupiter |
Source: NASA – Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Galileo Mission (1995–2003).