
Image description: The phases of the Moon follow each other in a 29.5-day cycle, called a "lunation." The 8 phases of the Moon are: full moon, first crescent moon, first quarter, gibbous moon, full moon, gibbous moon, last quarter, and last crescent moon. Solar eclipses occur at the new moon, and lunar eclipses occur at the full moon. Image source: astronoo.com
An eclipse requires an alignment of three celestial bodies: the Sun, the Earth, and the Moon.
Lunar eclipses are occultations of the Moon by the Earth's shadow, while solar eclipses are occultations of the Sun by the Moon's shadow. These celestial alignments are frequently observed, with at least one of each (lunar eclipse and solar eclipse) every 6 months.
The Moon appears to us in different phases, i.e., with different illuminations of the lunar sphere. This is due to the Moon's rotation around the Earth and the relative positions of the Sun, Earth, and Moon, which are in constant motion.
Since the Moon only reflects the Sun's light, the only visible part of the Moon is the part that is oriented both towards the Earth and towards the Sun.
The periodicity of the Moon's phases is 29.5 days, i.e., one lunation or lunar month, although there are several lunar months. Eclipses occur at syzygies, i.e., when there is an almost perfect alignment between the Sun, the Earth, and the Moon.
Solar eclipses occur at the new moon, and lunar eclipses occur at the full moon.
The ratio between the diameter of the Sun (1,400,000 km) and the diameter of the Moon (3,500 km) is approximately 1/400th, and the ratio between the distance of the Sun (149,600,000 km) and the distance of the Moon (384,000 km) is also approximately 1/400th. Since the Sun is 400 times larger and 400 times farther than the Moon, their apparent sizes in the sky are almost identical (≈0.5° or ≈30 minutes of angle). In reality, the apparent size of the Moon varies between 29.3' and 33.5', and the apparent size of the Sun varies between 31.5' and 32.5'.
This temporal coincidence is the basis for the mythological interpretations of certain civilizations, as the Moon sometimes perfectly masks the Sun.
Today, a total solar eclipse arouses the passion of crowds. Some enthusiasts are called "eclipse chasers"; they track eclipses all around the world. However, this coincidence will disappear; in hundreds of millions of years, there will only be annular eclipses because the Moon is moving away from the Earth by 4 cm per year.
The sidereal revolution period of the Moon is measured relative to the stars. It is the time required for the Moon to return to the same position relative to a star, as seen from Earth. This sidereal revolution period is 27.321582 days.
The synodic revolution period, measured this time relative to the Sun, is 29.530589 days. This explains why solar eclipses and lunar eclipses follow each other with an interval of approximately 15 days.
If the sidereal revolution period of the Moon is shorter than the synodic revolution period, it is because during a month, the Earth has advanced on its orbit, and it will take the Moon about 2 more days to reach the same position relative to the Sun.
The phenomenon is the same for the Earth, whose sidereal period (relative to the stars) is shorter than the synodic period (relative to the Sun) by about 4 minutes, i.e., approximately 23H 56mn or 0.99726968 days. The synodic period is longer by 1/365th because in 24 hours, the Earth has advanced on its orbit around the Sun by 1/365th. 1/365th of 24 hours is approximately 4 minutes.
Although the synodic revolution period is 29.5 days, eclipses do not occur every month. The Moon passes above or below the Sun because the plane of the Moon's orbit around the Earth and the plane of the Earth's orbit around the Sun (ecliptic) do not coincide; they form an angle of approximately 5.145°.
If the Moon moved around the Earth in the same plane as the Earth around the Sun, i.e., on the plane of the ecliptic, there would be a lunar eclipse at each full moon and a solar eclipse at each new moon, every 29.5 days, each separated by 15 days.
In fact, the alignments of the three celestial bodies can only occur if the Moon is very close to the plane of the ecliptic. This is why this plane has been named thus, in relation to the eclipse.
The point where the Moon passes above the plane of the ecliptic is called the ascending node, and conversely, the point where the Moon passes below the plane of the ecliptic is called the descending node.
To witness a total or partial eclipse, the Moon must be on the line of nodes; this is the only place where the alignment of the three celestial bodies is perfect. Therefore, there are between four and six eclipses in a year, at least two solar and at least two lunar.
In summary, eclipses occur during syzygies (alignment of the three celestial bodies) close to the line of nodes. Around the passage of the nodes, there is a period of 35 days during which an eclipse can occur. In 34.5 days, it is possible to observe two solar eclipses or two lunar eclipses, as the lunation lasts 29.5 days. Therefore, eclipses are spaced approximately one month or five to six months apart.
The Earth-Moon distance varies between 363,104 km and 405,696 km. The farther the Moon is from the Earth at the time of syzygy, the more partial the eclipse. The interval between two total solar eclipses of the same season (e.g., from one summer to the next) is generally 12 lunations, i.e., 354.4 days (1 year - 11 days). Thus, we were able to witness a total eclipse in Mongolia on August 1, 2008, then a total eclipse in China on July 22, 2009, and finally a total eclipse in Polynesia on July 11, 2010.
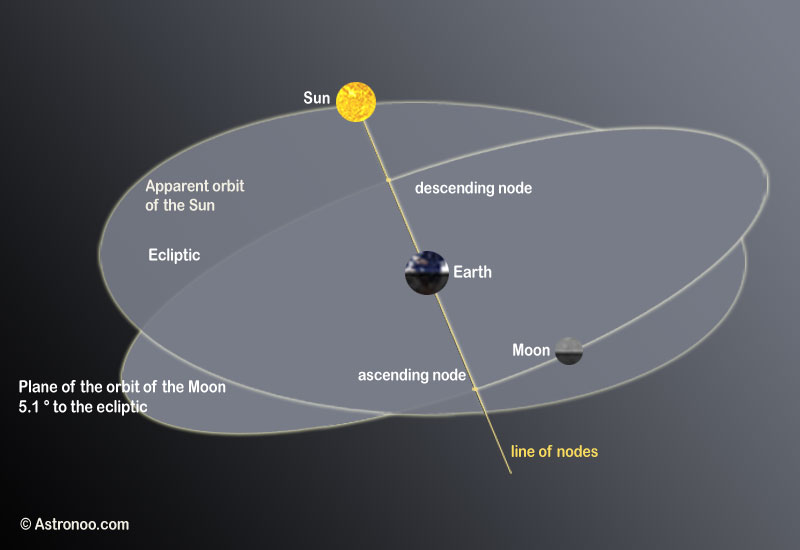
Plane of the apparent orbits of the Moon and the Sun, as seen from Earth. If the Moon moved around the Earth in the same plane as the Earth around the Sun, i.e., on the plane of the ecliptic, there would be a lunar eclipse at each full moon and a solar eclipse at each new moon, every 29.5 days, each separated by 15 days.
The eclipse period lasts 34.5 days, so there are 2 or 3 eclipses during this period. There are also 1.5 or 6 months between two consecutive solar or lunar eclipses. The alignments of the three celestial bodies can only occur if the Moon is very close to the plane of the ecliptic. This is why this plane has been named thus, in relation to the eclipse.
The plane of the Moon's orbit is animated by a precession movement; thus, the nodes traverse the ecliptic in the retrograde direction (clockwise) following a period of 18.61 years. Image source: astronoo.com