Asteroids, the threat...
Our most close neighbours
The interplanetary space is far from being empty, it is sprinkled with dusts and with mater dating the creation of the solar system.
Asteroids and comets, metal and rocky objects, move in a vertiginous speed around planets and around our Sun. Sometimes their orbits cross that of the planet or the Earth so provoking a collision, the energy loosened by the impact is terrifying. Meteorites and comets bombard our planet since the birth of the solar system. Although they seem wisely installed on their orbits between Mars and Jupiter, they are sometimes destructive and we owe them credibly the appearance of the life on Earth.
Asteroids being our most close neighbors, they are somehow, bound to our fate. Those who cross our orbit are called geocruisers. Astronomers considered the trajectories of asteroids susceptible to terminate millions of human lives on our planet. Apophis is an asteroid of small size because it is 250 meters wide and could represent a threat. We estimate at present at a chance on 45 000 the probability that this pebble comes to crash in the Pacific Ocean on April 13th, 2036.
NEOs are continuously monitored by an automated system (Sentry), which analyzes the most dangerous asteroids and considers the possibilities of future impact with Earth, over the next 100 years.
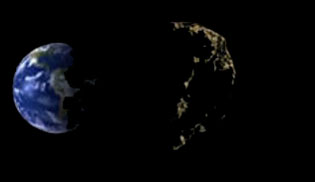
What an asteroid?
An asteroid is a not observable heavenly object in the bare eye because of its small size which varies some tens of meters in several hundreds kilometers in diameter. They are a part of our solar system and turn around Him. The objects of less than 50 m of diameter are called by meteorites. Those are not satellites of planets but fragments of the disk proto planetary which did not manage to group together in planets during their formation. Asteroids have a big importance in the understanding of the formation of the solar system, it is for that reason that the astronomers show a strong interest in the study of these objects. The first asteroid was accidentally discovered on December 31st, 1800 by Giuseppe Piazzi, director, in the period, of the observatory of Palermo, in Sicily. While observing the constellation of the Taurus, he perceived a not identified object moving very slowly in the night-sky.
His colleague, Carl Friedrich Gauss determined the exact distance of this unknown object and placed this celestial body between planets Mars and Jupiter.
Piazzi named him Ceres, of the name of the Greek goddess who makes take out the sap of the ground and who grows the young shoots in spring. Between 1802 and 1807, three other bodies were discovered: Pallas, Juno and Vesta.
In 1868, 100 asteroids were known. The 1000th approved discovery took place in 1921 and 10 000th in 1989. In March, 2006, there were 129 436 approved asteroids. The NEAR Shoemaker probe (Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous) was launched on February 17th, 1996 by the NASA to study in detail Eros, one of the biggest near-Earth object (NEO). This probe gave a complete cartography of Eros in 2000, it finally settled without damage on the asteroid, February 12th, 2001 and sent its last signal on February 28, 2001.
Image: The details of Eros seen by the probe NEAR which settled without damage on the asteroid, on February 12th, 2001.
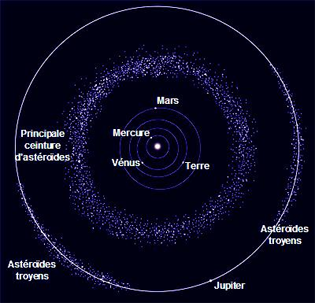
Zones with asteroids
Between Mars and Jupiter (from 300 to 600 million km of the Sun).
Asteroids are mainly situated in the main belt, between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. We find several hundreds of thousand listed objects there. All its objects would have been able to form a planet in this zone but the gravitational disturbances of Jupiter did not allow it. Jupiter played defender's role of the life on our planet. Without Jupiter, the bombardment on Earth would be 1000 times as frequent.
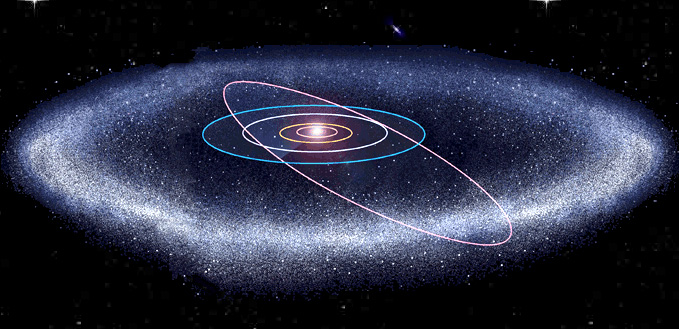
In the belt of Kuiper (between 35 and 100 UA of the Sun).
This zone contains ice-cold objects, and are not thus strictly speaking asteroids. This belt is rather a crèche of comets. The first member is discovered in 1992.
We count a little more than 1000 today.
The British call the asteroids of this type of "cubewanos".
The biggest identified until today is Quaoar (1280 km in diameter).
In the cloud of Oort (between 20000 and 150000 UA neighborhood).
This zone of the sky, the remainder of the original nebula, would contain billions of nuclei of comets and would be the source of most of the new comets which enter the central regions of the solar system.
The Cloud of Oort constitutes the reservoir of comets in long period. It is one diameter 1 000 time superior in that of the solar system that we know with the 8 planets.

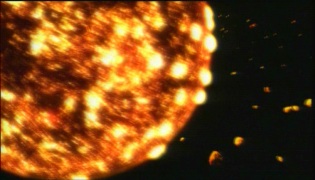
The big bombardment
It falls even today on the surface of the Earth several thousand tons of mater from the space. It is about interplanetary dusts.
Others are bigger, but their number became very weak if we compare it its being in the formation of the Solar system.
During the formation of planets, while their surface was semi liquid, millions of meteorites blocked the space.
Their impacts with the other objects of the solar system are responsible for craters which we observe everywhere on the telluric objects of the Solar system.
This big bombardment lasted several hundreds of million years and contributed to form planets.
The threat...
The risk of a major impact began to invade the consciences at the beginning of 1980s, when the scientific community had the first proofs that such a cataclysm had already occurred repeatedly in the story of the Earth.
At the beginning of 1990s, the astrophysicists understood that the stability which reigns in our solar system was only visible, when the French astronomer Jacques Laskar demonstrated that the movement of bodies in the space followed the laws of the chaos. Consequences is that it is impossible to foresee in the long term the trajectories of the objects which populate our solar system.
It already arrived several times and the life every time, disappeared in 90%. The geologists demonstrated that the cause was there, a collision with an asteroid. We know how to estimate this risk today.
In several hundreds of km off Mexico, on April 23rd, 2001, a meteorite of 5 m of diameter wasted away above the Pacific Ocean. Its explosion at high height in the atmosphere loosened an equivalent energy in the middle of the bomb of Hiroshima.
Let us imagine that this object measured 50 meters, then the explosion would have been one thousand more violent times, without any time to provoke a disaster because it would have wasted away in high height.
Let us enlarge the object by 10, it makes then 500 meters in diameter. The energy to be dissipated is 1 million bigger times. The atmosphere would then be pierced and the object would provoke a gigantic tidal wave killing several hundreds of thousand persons on the American and Asian coasts. With 5 kilometers in diameter its impact would be a more powerful billion times and would have engendered an apocalypse deserving of the worst divine punishments.
Nevertheless the risks of collision between these objects and the Earth if they are more and more rare, are not null.
Disintegration of meteorites...
An asteroid of 1 to 3 meters in diameter that enters the atmosphere does not cause any damage because a total disintegration occurs during passage through the atmosphere.
Asteroid 2008 TC3 entered the atmosphere with a low incidence angle (19 degrees) and low relative speed (12.8 km/second), 7 October 2008 to 2 h 46 UTC Time (UTC or in English UT).
2008 TC3 is special because it has been observed even before his fall to Earth.
Until a few meters in diameter, these objects are not daunting to our planet Earth.
They are monitoring programs that have the sky tracked object and to predict with precision the date and place of his fall in the Nubian Desert in Sudan.
Its fragility and porosity all have surprised scientists.
The explosion of an asteroid 10 meters over Indonesia occurred October 8, 2009 in the upper atmosphere at an altitude of 15 to 20 kilometers.
It has caused no damage to the ground despite a power equivalent to 3 times the nuclear bomb that devastated Hiroshima in 1945 (approximately 50 000 tons of TNT).
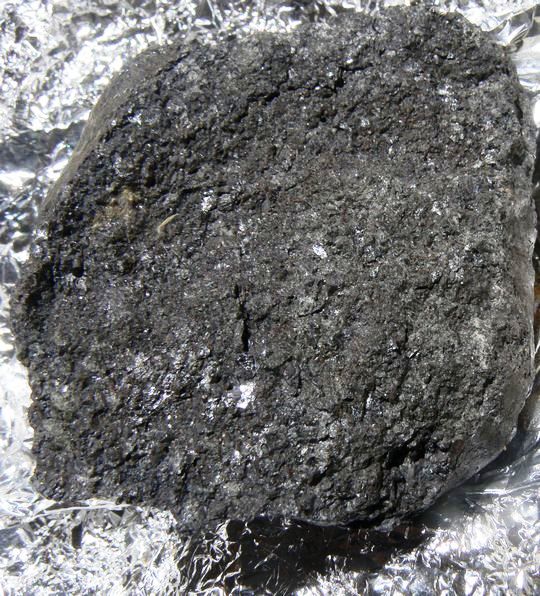

Image: Asteroid against this, weighed 80 tones with a diameter of about 4.1 meters.
It was too small to cause damage on the ground.
It disintegrated at 37 km altitude in the atmosphere betraying its fragile nature, leaving little hope of retrieving fragments.
However Peter Jenniskens (SETI Institute, California) and Muawia Shaddad fetched meteorites in the desert of Nubia with students from the University of Khartoum. 47 meteorites were recovered, with a total weight of 3.95 kg.
Age = recent, Diameter of the crater = small traces,
Diameter of the meteorite = 1 in 3 meters
No damage...
An asteroid 60 meters in diameter which enters the atmosphere with a too weak angle of incidence (some degrees), does not manage to cross the atmosphere and does not provoke damage.
It bounces simply on the atmospheric layer of the Earth and leaves in the space.
It occurred on 10/08/1972 in the sky of the Montana in the North of the United States.

Image: This meteorite is in fact a small asteroid 60 meters in diameter, which crossed the sky of the Montana on August 10th, 1972 before bouncing on the atmosphere and getting lost in the space.
Credit Nasa
Age = 40 years,
Diameter of the crater = 0 meters,
Diameter of the meteorite = 60 meters
Once every 1 000 years...
An asteroid 75 meters in diameter would provoke a crater 1700 meters in diameter and would destroy a city as Paris by killing 5000 persons.
The probability that it arrives is once every 1 000 years.
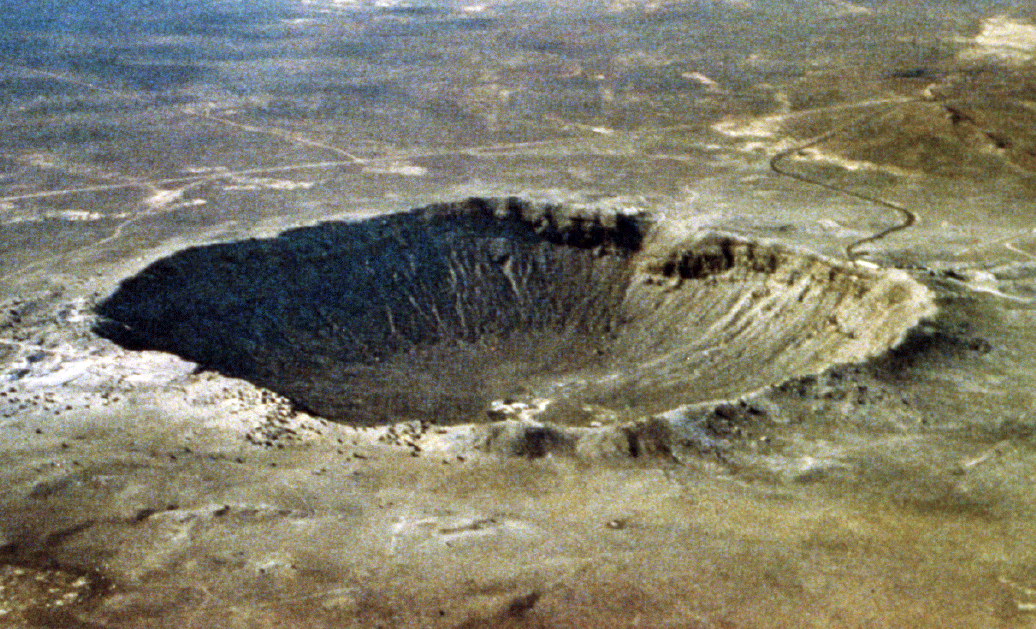

Image: Meteor Crater, Arizona. Wikimedia Commons
Age = 50 000 years,
Diameter of the crater = 1500 meters, (200 meters deep and 50 meters high).
Diameter of the meteorite = 75 meters
Once every 45 000 years...
An asteroid 350 meters in diameter would provoke a crater 6000 meters in diameter and would destroy a zone as Ile-de-France by killing 500 000 persons.
The probability that it arrives is once every 16 000 years. Apophis (250 meters) could be the next threat. We estimate at present at a chance on 45 000 the probability that it comes to crash in the Pacific Ocean on April 13th, 2036.

Image: The crater filled with water of Sääksjärvi in Finland
Age = 560 million years,Diameter of the crater = 6 kilometers,
Diameter of the meteorite = 300 meters
Once every 63 000 years...
An asteroid 700 meters in diameter would provoke a crater 12 kilometers in diameter and would destroy a zone as a quarter of France by killing 1,5 billion persons because of the tsunami activated on the scale of a ground hemisphere.
The probability that it arrives is once every 63 000 years.

Image: The crater filled with water of Dellen in Sweden.
Age = 89 million years,Diameter of the crater = 19 kilometers,
Diameter of the meteorite = 1 km.
Once every 250 000 years...
An asteroid 1700 meters in diameter would provoke a crater 30 kilometers in diameter and would destroy a zone as France by killing 1,5 billion persons because of the tsunami activated on the scale of a ground hemisphere and of the modification of the climate which would follow itself with disappearance of the ozone layer.
The probability that it arrives is once every 250 000 years.
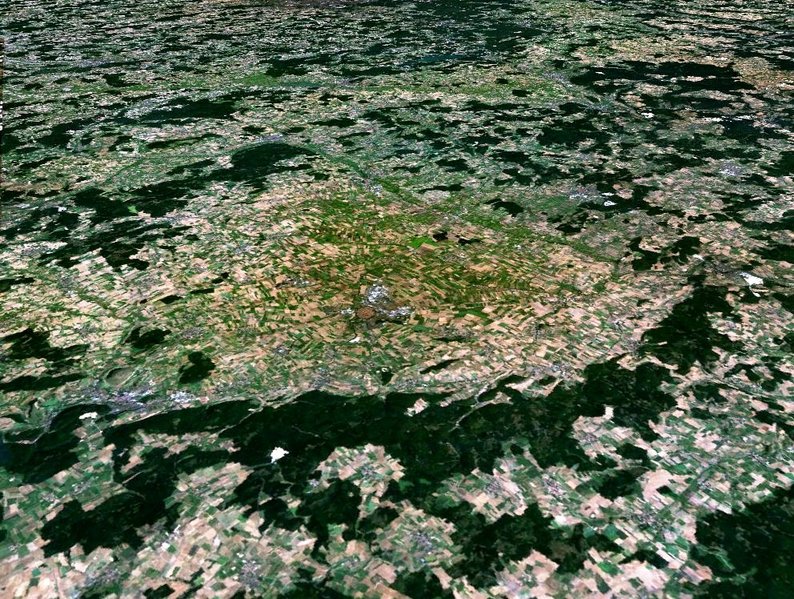

Image: Ries Crater in Germany. The stones of the Church of Nordlingen, located at the center of the Ries crater, was carved into a rock called impact suevite (rock formed by meteorite impact on Earth).
Age = 15 million years,Diameter of the crater = 24 kilometers,
Diameter of the meteorite = 1,2 km.
Once every 1 000 000 years...
An asteroid 3 kilometers in diameter would provoke a crater 60 kilometers in diameter and would destroy a zone as France and its nearby countries by killing 2,5 billion persons because of the tsunami activated on the scale of a ground hemisphere, of the modification of the climate and the fires.
The probability that it arrives is once all the million years.
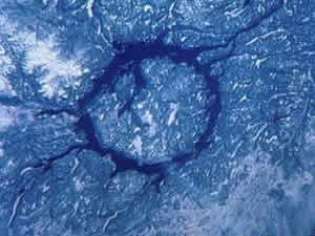
Image: Crater of Manicouagan, Quebec.
Age = 210 million years, average
Diameter of the crater = 80 km, what corresponds to a meteorite of diameter 3,5 km
source: site Planet Earth
Once every 10 000 000 years...
An asteroid 7 kilometers in diameter would provoke a crater 125 kilometers in diameter and would destroy a zone as Europe by killing 3 billion persons because of the tsunami activated on the scale of a ground hemisphere, of the modification of the long-term climate and the fires.
The probability that it arrives is once every 10 million years. We reach here an extinction of mass.

Image: Crater of Popigai, Siberia.
Age = 40 million years, average
Diameter of the crater = 100 km,
Diameter of the Meteorite = 5 km
source: Alpha Centauri's Universe
Once every 65 000 000 years...
An asteroid 16 kilometers in diameter would provoke a crater 200 kilometers in diameter and would have a world repercussion by killing 6 billion persons because tsunami activated on the scale of the planet, and modification of the climate with very long term.
The probability that it arrives is of time every 100 million years. Extinction of mass as the one that there was there is 65 million years provoking the disappearance of dinosaurs and 90 % of the sorts.
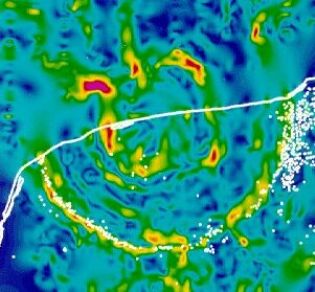
Image: Crater of Chicxulub, Mexico
Age = 65 million years, average
Diameter = 200 km,
Diameter of the meteorite = 10 km.
source: site MIAC Gravimetry
Conclusion
Millions of asteroids frequent the region of the space between Mars and Jupiter.
The belt of Kuiper it is more than one thousand billion comets and at least so much in the cloud of Oort.
All these objects undergo the laws of the flight mechanics and their ballet around the Sun is chaotic by nature. The slightest disturbance is enough to upset their orbit. An asteroid just has for example to undergo one small disturbance in passing near a satellite of Jupiter so that its trajectory is dangerously diverted in the direction of the Earth. It is probably one of them which will strike the Earth some day...

Image: Artist image
Articles on the same theme
1997 © Astronoo.com − Astronomy, Astrophysics, Evolution and Ecology.
"The data available on this site may be used provided that the source is duly acknowledged."
How Google uses data
Legal mentions
English Sitemap − Full Sitemap
Contact the author
 Yarkovsky Effect on Asteroids
Yarkovsky Effect on Asteroids  Arrokoth, the
red snowman
Arrokoth, the
red snowman  The Kirkwood Gaps in the Main Asteroid Belt
The Kirkwood Gaps in the Main Asteroid Belt  What is the asteroid belt?
What is the asteroid belt?  The Great Comet of 1577 Shattered the Crystal Spheres
The Great Comet of 1577 Shattered the Crystal Spheres  Asteroids, the threat to life...
Asteroids, the threat to life...  Meteorites, extraterrestrial objects
Meteorites, extraterrestrial objects  Hartley 2 passes by us, every 6 years
Hartley 2 passes by us, every 6 years  Collision between 2 asteroids
Collision between 2 asteroids  2005 YU55: The 400 m Asteroid that Grazed Earth
2005 YU55: The 400 m Asteroid that Grazed Earth  Asteroid Apophis: The Perfect Candidate for a Global Impact?
Asteroid Apophis: The Perfect Candidate for a Global Impact?  The asteroid
Vesta
The asteroid
Vesta  What
is an asteroid?
What
is an asteroid?  2012 and Comet ISON: Between Promise of Brilliance and Disappointment
2012 and Comet ISON: Between Promise of Brilliance and Disappointment  Giants of the Asteroid Belt: Classification by Size
Giants of the Asteroid Belt: Classification by Size  Impact
craters on Earth
Impact
craters on Earth  Online Simulator: Orbits of Asteroids
Online Simulator: Orbits of Asteroids  Online Simulator: Orbits of Near-Earth Asteroids
Online Simulator: Orbits of Near-Earth Asteroids  Rosetta has a date with a comet
Rosetta has a date with a comet  Near-Earth asteroids
Near-Earth asteroids  Asteroid 2009 DD45 sends us a sign
Asteroid 2009 DD45 sends us a sign  Where does the water on planet Earth come from?
Where does the water on planet Earth come from?  Asteroid
or comet?
Asteroid
or comet?  2010 TK7, Earth's Trojan asteroid
2010 TK7, Earth's Trojan asteroid  Turin Scale: A Classification of Impact Risks
Turin Scale: A Classification of Impact Risks  Nice model, the late bombardment
Nice model, the late bombardment  Once again we haven't seen it
Once again we haven't seen it  Comet Lemmon 2013: A Celestial Visitor from the Southern Hemisphere
Comet Lemmon 2013: A Celestial Visitor from the Southern Hemisphere  Asteroid 2012 DA14 passed on February 15, 2013
Asteroid 2012 DA14 passed on February 15, 2013 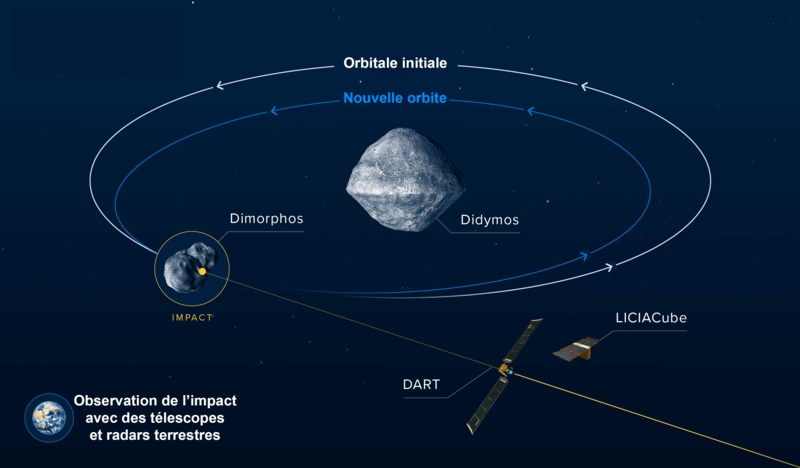 Planetary defense with Didymos and Dimorphos
Planetary defense with Didymos and Dimorphos 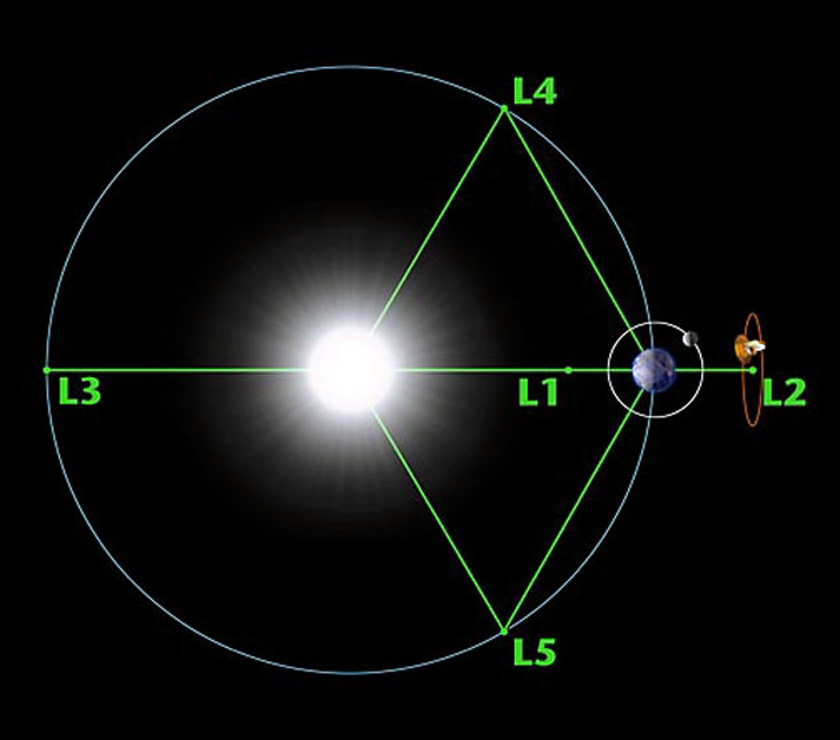 Lagrange points, L1 L2 L3 L4 L5
Lagrange points, L1 L2 L3 L4 L5  Chariklo and his two amazing rings
Chariklo and his two amazing rings  Rosetta
and Philae
Rosetta
and Philae  Kuiper Belt Objects
Kuiper Belt Objects  Ceres,
the largest asteroid
Ceres,
the largest asteroid  The periodic passage of comets
The periodic passage of comets  Vesta and its Curiosities: The Enigma of the Torn South Pole
Vesta and its Curiosities: The Enigma of the Torn South Pole  Orbits of Near-Earth Asteroids: When Asteroids Brush Past Earth
Orbits of Near-Earth Asteroids: When Asteroids Brush Past Earth  Wandering
comets
Wandering
comets  Asteroid Juno: an unknown giant of the solar system
Asteroid Juno: an unknown giant of the solar system  Ganymed (1036): Near-Earth and Mars-crosser
Ganymed (1036): Near-Earth and Mars-crosser  Hell
of the Hadean
Hell
of the Hadean 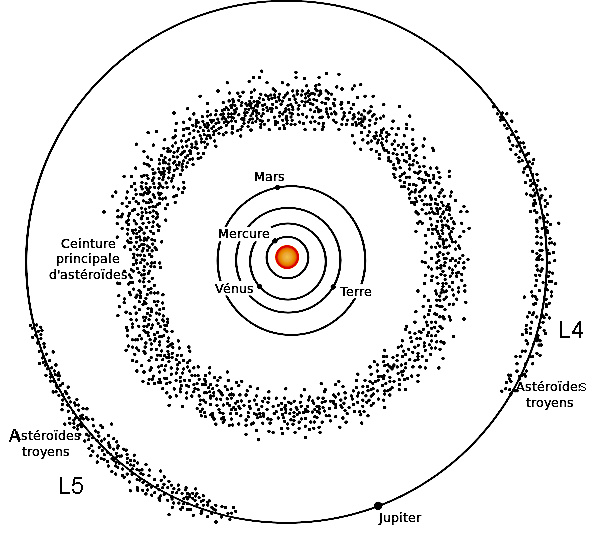 Are there natural satellites of natural satellites?
Are there natural satellites of natural satellites?  Earth's quasi-satellite: 2016 HO3
Earth's quasi-satellite: 2016 HO3